Home > Press > New milestone could help magnets end era of computer transistors
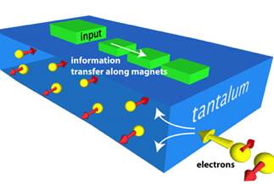 |
| As current passes through a strip of tantalum, electrons with opposite spins separate. Researchers used the resulting polarization to create a nanomagnetic switch that could one day replace computer transistors. Image by Debanjan Bhowmik, UC Berkeley |
Abstract:
New work by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, could soon transform the building blocks of modern electronics by making nanomagnetic switches a viable replacement for the conventional transistors found in all computers.
New milestone could help magnets end era of computer transistors
Berkeley, CA | Posted on November 18th, 2013Semiconductor-based transistors, the on-off switches that direct the flow of electricity and form a computer's nervous system, have been consuming greater chunks of power at increasingly hotter temperatures as processing speeds grow. For more than a decade, researchers have been pursuing magnets as an alternative to transistors because they require far less energy needs when switching. However, until now, the power needed to generate the magnetic field to orient the magnets so they can easily clock on and off has negated much of the energy savings that would have been gained by moving away from transistors.
UC Berkeley researchers overcame this limitation by exploiting the special properties of the rare, heavy metal tantalum.
In a paper published online Sunday, Nov. 17, in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, the researchers describe how they created a so-called Spin Hall effect by using nanomagnets placed on top of tantalum wire and then sending a current through the metal. Electrons in the current will randomly spin in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. When the current is sent through tantalum's atomic core, the metal's physical properties naturally sort the electrons to opposing sides based on their direction of spin. This creates the polarization researchers exploited in order to switch magnets in a logic circuit without the need for a magnetic field.
"This is a breakthrough in the push for low-powered computing," said study principal investigator Sayeef Salahuddin, UC Berkeley assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences. "The power consumption we are seeing is up to 10,000 times lower than state-of-the-art schemes for nanomagnetic computing. Our experiments are the proof of concept that magnets could one day be a realistic replacement for transistors."
Other co-authors of the study are graduate student and lead author Debanjan Bhowmik, and Long You, a research scholar.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, Semiconductor Research Corp. and the National Science Foundation helped support this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Sarah Yang
Media Relations
(510) 643-7741
Sayeef Salahuddin
(510) 642-4662
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








