Home > Press > Graphene with aroma: New production method broadens the perspectives for an improved use of the "magic material" - many different forms are possible
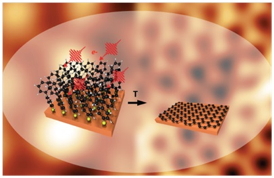 |
| The cover picture of the scientific journal "Advanced Materials" gives a schematic representation of the conversion of the monolayer of the complex molecule biphenyl thiol in the two-dimensional graphene crystal by electron irradiation and thermal treatment. Fig.: Advanced Materials 25 (2013). Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Reproduced with permission. |
Abstract:
Graphene, a crystal composed of only one layer of carbon atoms arranged in a regular hexagon, is regarded as a material which is believed to be capable of performing miracles, in particular in the fields of electronics, sensor technology and display technology, but also in metrology. Only four years after the first successful preparation of graphene, its discoverers Geim and Novoselov were therefore awarded a Nobel Prize. As the original preparation method (flaking of single atomic layers of graphite) does not offer a good perspective for broad technological use, many groups of researchers are concentrating very strongly on the development of alternative manufacturing procedures. A completely new and very flexible variant has now been developed by the group of Andrey Turchanin from the University of Bielefeld in cooperation with the University of Ulm and three departments of the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) and this has been published in the scientific journal "Advanced Materials".
Graphene with aroma: New production method broadens the perspectives for an improved use of the "magic material" - many different forms are possible
Bielefeld, Germany | Posted on October 2nd, 2013 In contrast to the conventional methods where graphene is manufactured, for example, by precipitation of carbon atoms from the gas phase or by thermal graphitization of silicon carbide, the scientists selected aromatic molecules as a starting point in this work. As substrates, both copper single-crystals and inexpensive polycrystalline copper foils were used. By irradiation with low-energy electrons and subsequent thermal annealing, it was then possible to convert a self-organized single-layer of the molecule biphenyl thiol, which had precipitated on the copper surface, into graphene.
To investigate the chemical and physical properties of the graphene manufactured in this way, different characterization methods from Ulm and Bielefeld universities and from PTB were applied, for example, scanning tunnelling microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy as well as electric transport measurements at low temperatures and high magnetic fields. All these measurements confirm that graphene of excellent crystalline and electronic quality had actually been manufactured from the aromatic molecule. The flexibility of the electron irradiation, which is possible both over large areas and also with excellent spatial resolution at small, well-defined places, now allows graphene structures of basically any form to be manufactured, e.g. quantum dots, nanoribbons or other nano-geometries with specific functionality. The selection of the temperature in the thermal conversion step also allows the degree of crystallinity and the characteristics of the graphene depending on it to be adjusted.
Additional advantages result from the versatility of the method of self-organized coating. It can be performed with different aromatic molecules which could, for example, also contain doping atoms for electronic doping of the final product. Applied in multiple layers, so-called bi-layer or multi-layer graphene could be manufactured, whose changed electronic band structure expands the potential applications of single-layer graphene. Likewise, other substrates than the copper used here (for example other metals, semiconductors, isolators) can be used. In addition, it should also be possible to manufacture graphene on any three-dimensional surfaces, as molecular self-organization also takes place on curved surfaces. The new manufacturing method broadens the perspectives for an improved use of the "magic material" in such an impressive way that the respective publication was emphasized on the cover sheet of the August issue of the scientific journal "Advanced Materials".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Franz Josef Ahlers
PTB Department 2.6 Electric Quantum Metrology
49-531-592-2600
PD Dr. Andrey Turchanin
University of Bielefeld
Faculty of Physics
Physics of Super-molecular Systems and Surfaces
Bielefeld Institute for Biophysics and Nanoscience (BINAS)
Universitätsstr. 25
33615 Bielefeld
phone: +49(521) 106-5376
Copyright © Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
Turning up the signal November 8th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








