Home > Press > Guided Growth of Nanowires Leads to Self-Integrated Circuits
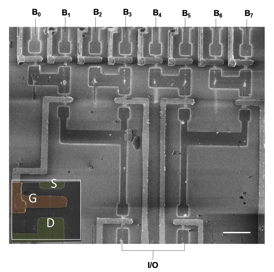 |
| SEM image of a logic circuit based on 14 nanowires |
Abstract:
Researchers working with tiny components in nanoelectronics face a challenge similar to that of parents of small children: teaching them to manage on their own. The nano-components are so small that arranging them with external tools is impossible. The only solution is to create conditions in which they can be "trusted" to assemble themselves.
Guided Growth of Nanowires Leads to Self-Integrated Circuits
Rehovot, Israel | Posted on July 31st, 2013Much effort has gone into facilitating the self-assembly of semiconductor nanowires, the basic building blocks of electronics, but until recently, success has been limited. Scientists had developed methods for growing nanowires vertically on a surface, but the resultant structures were short and disorganized. After growing, such nanowires need to be "harvested" and aligned horizontally; since such placement is random, scientists need to determine their location and only then integrate them into electric circuits.
A team led by Prof. Ernesto Joselevich of the Weizmann Institute's Materials and Interfaces Department has managed to overcome these limitations. For the first time, the scientists have created self-integrating nanowires whose position, length and direction can be fully controlled.
The achievement, reported today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), USA, was based on a method developed by Joselevich two years ago for growing nanowires horizontally in an orderly manner. In the present study - conducted by Joselevich with Dr. Mark Schvartzman and David Tsivion of his lab, and Olga Raslin and Dr. Diana Mahalu of the Physics of Condensed Matter Department - the scientists went further, creating self-integrated electronic circuits from the nanowires.
First, the scientists prepared a surface with tiny, atom-sized grooves and then added to the middle of the grooves catalyst particles that served as nuclei for the growth of nanowires. This setup defined the position, length and direction of the nanowires. They then succeeded in creating a transistor from each nanowire on the surface, producing hundreds of such transistors simultaneously. The nanowires were also used to create a more complex electronic component - a functioning logic circuit called an Address Decoder, an essential constituent of computers. These ideas and findings have earned Joselevich a prestigious European Research Council Advanced Grant.
"Our method makes it possible, for the first time, to determine the arrangement of the nanowires in advance to suit the desired electronic circuit," Joselevich explains. The ability to efficiently produce circuits from self-integrating semiconductors opens the door to a variety of technological applications, including the development of improved LED devices, lasers and solar cells.
Prof. Ernesto Joselevich's research is supported by the Carolito Stiftung and the European Research Council.
####
About Weizmann Institute
The Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, is one of the world's top-ranking multidisciplinary research institutions. Noted for its wide-ranging exploration of the natural and exact sciences, the Institute is home to scientists, students, technicians and supporting staff. Institute research efforts include the search for new ways of fighting disease and hunger, examining leading questions in mathematics and computer science, probing the physics of matter and the universe, creating novel materials and developing new strategies for protecting the environment.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Weizmann Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








