Home > Press > Graphene 'onion rings' have delicious potential: Rice University lab grows 'bottom-up' nanoribbons for the first time
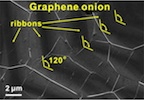 |
| An electron microscope image of graphene "onion rings" shows the concentric, dark ribbons through the overlying sheet of graphene. The ribbons follow the form of the growing graphene sheet, which takes the shape of a hexagon. Credit: Tour Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Concentric hexagons of graphene grown in a furnace at Rice University represent the first time anyone has synthesized graphene nanoribbons on metal from the bottom up -- atom by atom.
Graphene 'onion rings' have delicious potential: Rice University lab grows 'bottom-up' nanoribbons for the first time
Houston, TX | Posted on July 18th, 2013As seen under a microscope, the layers brought onions to mind, said Rice chemist James Tour, until a colleague suggested flat graphene could never be like an onion.
"So I said, ‘OK, these are onion rings,'" Tour quipped.
The name stuck, and the remarkable rings that chemists marveled were even possible are described in a new paper in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The challenge was to figure out how such a thing could grow, Tour said. Usually, graphene grown in a hot furnace by chemical vapor deposition starts on a seed -- a speck of dust or a bump on a copper or other metallic surface. One carbon atom latches onto the seed in a process called nucleation and others follow to form the familiar chicken-wire grid.
Experiments in Tour's lab to see how graphene grows under high pressure and in a hydrogen-rich environment produced the first rings. Under those conditions, Tour, Rice theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson and their teams found that the entire edge of a fast-growing sheet of graphene becomes a nucleation site when hydrogenated. The edge lets carbon atoms get under the graphene skin, where they start a new sheet.
But because the top graphene grows so fast, it eventually halts the flow of carbon atoms to the new sheet underneath. The bottom stops growing, leaving a graphene ring. Then the process repeats.
"The mechanism relies on that top layer to stop carbon from reaching the bottom so easily," Tour said. "What we get are a multiple of single crystals growing one on top of the other."
The Tour lab pioneered the bulk manufacture of single-atom-thick graphene nanoribbons in 2009 with the discovery that carbon nanotubes could be chemically "unzipped" into long, thin sheets. Nanoribbons are being studied for use in batteries and advanced electronics and as heat sinks.
"Usually you make a ribbon by taking a large thing and cutting it down," Tour said. "But if you can grow a ribbon from the bottom up, you could have control of the edges." The atomic configuration at the edge helps determine graphene's electrical properties. The edges of hexagonal graphene onion rings are zigzags, which make the rings metallic.
"The big news here," he said, "is that we can change relative pressures of the growth environment of hydrogen versus carbon and get entirely new structures. This is dramatically different from regular graphene."
Graduate student Zheng Yan, a member of Tour's lab and lead author of the paper, discovered the new route to nanoribbons while experimenting with graphene growth under hydrogen pressurized to varying degrees. The sweet spot for rings was at 500 Torr, he said.
Further testing found the microscopic rings formed underneath and not on top of the sheet, and Yakobson's lab confirmed the growth mechanism through first-principle calculations. Yan also determined the top sheet of graphene could be stripped away with argon plasma, leaving stand-alone rings.
The width of the rings, which ranged from 10 to 450 nanometers, also affects their electronic properties, so finding a way to control it will be one focus of continued research, Tour said. "If we can consistently make 10-nanometer ribbons, we can begin to gate them and turn them into low-voltage transistors," he said. They may also be suitable for lithium storage for advanced lithium ion batteries, he said.
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students Yuanyue Liu, Zhiwei Peng, Changsheng Xiang, Abdul-Rahman Raji and Errol Samuel; postdoctoral researchers Jian Lin, Gunuk Wang and Haiqing Zhou; Rice alumna Elvira Pembroke; and Professor Ting Yu of Nanyang Technological University. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and of computer science at Rice. Yakobson is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science and professor of chemistry.
The Singapore National Research Foundation, the Office of Naval Research, the Lockheed Martin LANCER IV program and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research supported the work. Calculations were performed on the National Science Foundation-supported DaVinCI supercomputer at Rice, the National Institute for Computational Sciences' Kraken and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center's Hopper.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








