Home > Press > Whispering light hears liquids talk: University of Illinois researchers build first-ever bridge between optomechanics and microfluidics
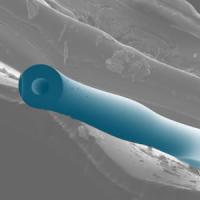 |
| This is a false-color SEM (scanning electron micrograph) of the microfluidic optomechanical resonator.
Credit: Gaurav Bahl, University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Ever been to a whispering gallery—a quiet, circular space underneath an old cathedral dome that captures and amplifies sounds as quiet as a whisper? Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign are applying similar principles in the development optomechanical sensors that will help unlock vibrational secrets of chemical and biological samples at the nanoscale.
Whispering light hears liquids talk: University of Illinois researchers build first-ever bridge between optomechanics and microfluidics
Urbana, IL | Posted on June 7th, 2013"Optomechanics is an area of research in which extremely minute forces exerted by light (for example: radiation pressure, gradient force, electrostriction) are used to generate and control high-frequency mechanical vibrations of microscale and nanoscale devices," explained Gaurav Bahl, an assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at Illinois.
In glass microcavities that function as optical whispering galleries, according to Bahl, these miniscule optical forces can be enhanced by many orders-of-magnitude, which enables 'conversations' between light (photons) and vibration (phonons). These devices are of interest to condensed matter physics as the strong phonon-photon coupling enables experiments targeting quantum information storage (i.e. qubits), quantum-mechanical ground state (i.e. optomechanical cooling), and ultra-sensitive force measurements past the standard quantum limit.
Researchers developed a hollow optomechanical device made of fused silica glass, through which fluids and gases could flow. Employing a unique optomechanical interaction called Brillouin Optomechanics (described previously in Bahl et al, Nature Communications 2:403, 2011; Bahl et al, Nature Physics, vol.8, no.3, 2012), the researchers achieved the optical excitation of mechanical whispering-gallery modes at a phenomenal range of frequencies spanning from 2 MHz to 11,000 MHz.
"These mechanical vibrations can, in turn, 'talk' to liquids within the hollow device and provide optical readout of the mechanical properties," said Bahl, who is first author of the paper, "Brillouin cavity optomechanics with microfluidic devices," published this week in Nature Communications.
By confining various liquids inside a hollow microfluidic optomechanical (μFOM) resonator, researchers built the first-ever bridge between optomechanics and microfluidics.
"We found that the optomechanical interaction in the μFOM device is dependent on the fluid contained within," Bahl said. "These results are a step towards novel experiments probing optomechanics on non-solid phases of matter. In particular, the high frequency, high quality-factor mechanical vibrations demonstrated in this work may enable strongly localized, high-sensitivity, optomechanical interaction with chemical and biological samples."
Potential uses for this technology include optomechanical biosensors that can measure various optical and mechanical properties of a single cell, ultra-high-frequency analysis of fluids, and the optical control of fluid flow.
In addition to Bahl, the paper's authors include Kyu Hyun Kim, Wonsuk Lee, Jing Liu, Xudong Fan, and Tal Carmon at the University of Michigan. Much of this work was performed while Bahl, who joined the Engineering at Illinois faculty in 2012, was a postdoctoral researcher in Carmon's lab. At Illinois, the Bahl research group continues this work, and is investigating this technology for building biosensors.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Gaurav Bahl
217-300-2194
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








