Home > Press > Researchers Stitch Defects into the World’s Thinnest Semiconductor
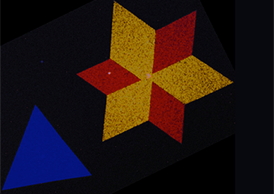 |
| A false-color electron microscopy image showing the star-shaped crystals in monolayers of two-dimensional semiconducting molybdenum disulfide. The red, yellow, and blue colors represent two dominant crystal orientations that are stitched together by a line of atomic defects. Image courtesy of Pinshane Y. Huang and David A. Muller |
Abstract:
In pioneering new research at Columbia University, scientists have grown high-quality crystals of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), the world's thinnest semiconductor, and studied how these crystals stitch together at the atomic scale to form continuous sheets. Through beautiful images of strikingly symmetric stars and triangles hundreds of microns across, they have uncovered key insights into the optical and electronic properties of this new material, which can be either conducting or insulating to form the basic "on-off switch" for all digital electronics. The study is published in the May 5, 2013, issue of Nature Materials.
Researchers Stitch Defects into the World’s Thinnest Semiconductor
New York, NY | Posted on May 22nd, 2013 "Our research is the first to systematically examine what kinds of defects result from these large growths, and to investigate how those defects change its properties," says James Hone, professor of mechanical engineering at Columbia Engineering, who led the study. "Our results will help develop ways to use this new material in atomically thin electronics that will become integral components of a whole new generation of revolutionary products such as flexible solar cells that conform to the body of a car."
This multidisciplinary collaboration by the Energy Frontier Research Center at Columbia University with Cornell University's Kavli Institute for Nanoscale Science focused on molybdenum disulfide because of its potential to create anything from highly efficient, flexible solar cells to conformable touch displays. Earlier work from Columbia demonstrated that monolayer MoS2 has an electronic structure distinct from the bulk form, and the researchers are excited about exploring other atomically thin metal dichalcogenides, which should have equally interesting properties. MoS2 is in a class of materials called transition metal dichalcogenides, which can be metals, semiconductors, dielectrics, and even superconductors.
"This material is the newest in a growing family of two-dimensional crystals," says Arend van der Zande, a research fellow at the Columbia Energy Frontier Research Center and one of the paper's three lead authors. "Graphene, a single sheet of carbon atoms, is the thinnest electrical conductor we know. With the addition of the monolayer molybdenum disulfide and other metal dichalcogenides, we have all the building blocks for modern electronics that must be created in atomically thin form. For example, we can now imagine sandwiching two different monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides between layers of graphene to make solar cells that are only eight atoms thick—20 thousand times smaller than a human hair!"
Until last year, the majority of experiments studying MoS2 were done by a process called mechanical exfoliation, which only produces samples just a few micrometers in size. "While these tiny specimens are fine for scientific studies," notes Daniel Chenet, a PhD in Hone's lab and another lead author, "they are much too small for use in any technological application. Figuring out how to grow these materials on a large scale is critical."
To study the material, the researchers refined an existing technique to grow large, symmetric crystals up to 100 microns across, but only three atoms thick. "If we could expand one of these crystals to the thickness of a sheet of plastic wrap, it would be large enough to cover a football field—and it would not have any misaligned atoms," says Pinshane Huang, a PhD student in the David Muller lab at Cornell and the paper's third lead author.
For use in many applications, these crystals need to be joined together into continuous sheets like patches on a quilt. The connections between the crystals, called grain boundaries, can be as important as the crystals themselves in determining the material's performance on a large scale. "The grain boundaries become important in any technology," says Hone. "Say, for example, we want to make a solar cell. Now we need to have meters of this material, not micrometers, and that means that there will be thousands of grain boundaries. We need to understand what they do so we can control them."
The team used atomic-resolution electron microscopy to examine the grain boundaries of this material, and saw lines of misaligned atoms. Once they knew where to find the grain boundaries, and what they looked like, the team could study the effect of a single grain boundary on the properties of the MoS2. To do this, they built tiny transistors, the most basic component in all of electronics, out of the crystals and saw that the single, defective line of atoms at the grain boundaries could drastically change the key electronic and optical properties of the MoS2.
"We've made a lot of progress in controlling the growth of this new ‘wonder' nanomaterial and are now developing techniques to integrate it into many new technologies," Hone adds. "We're only just beginning to scratch the surface of what we can make with these materials and what their properties are. For instance, we can easily remove this material from the growth substrate and transfer it on to any arbitrary surface, which enables us to integrate it into large-scale, flexible electronics and solar cells."
The crystal synthesis, optical measurements, electronic measurements, and theory were all performed by research groups at Columbia Engineering. The growth and electrical measurements were made by the Hone lab in mechanical engineering; the optical measurements were carried out in the Tony Heinz lab in physics. The structural modeling and electronic structure calculations were performed by the David Reichman lab in chemistry. The electron microscopy was performed by atomic imaging experts in the David Muller lab at Cornell University's School of Applied and Engineering Physics, and the Kavli Institute at Cornell for Nanoscale Science.
The study was sponsored by the Columbia Energy Frontier Research Center, with additional support provided by the National Science Foundation through the Cornell Center for Materials Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Holly Evarts
Director
Strategic Communications and Media Relations
347-453-7408 (c)
212-854-3206 (o)
Copyright © Columbia Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








