Home > Press > Add boron for better batteries: Rice University theorists say graphene-boron mix shows promise for lithium-ion batteries
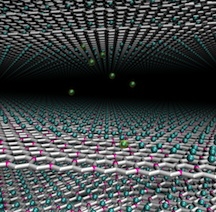 |
| A theory developed at Rice University determined that a graphene/boron compound would excel as an ultrathin anode for lithium-ion batteries. The compound would store far more energy than graphite electrodes used in current batteries. Credit: Vasilii Artyukhov/Rice University |
Abstract:
Frustration led to revelation when Rice University scientists determined how graphene might be made useful for high-capacity batteries.
Add boron for better batteries: Rice University theorists say graphene-boron mix shows promise for lithium-ion batteries
Houston, TX | Posted on May 17th, 2013Calculations by the Rice lab of theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson found a graphene/boron anode should be able to hold a lot of lithium and perform at a proper voltage for use in lithium-ion batteries. The discovery appears in the American Chemical Society's Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
The possibilities offered by graphene get clearer by the day as labs around the world grow and test the one-atom-thick form of carbon. Because it is as thin as possible, battery manufacturers hope to take advantage of graphene's massive surface area to store lithium ions. Counting both sides of the material, one gram would cover 2,630 square meters, or nearly half a football field.
But there's a problem. The ions don't stick to graphene very well.
"As often happens with graphene, people oversold how wonderful it would be to absorb lithium," said Yakobson, whose group analyzes relationships between atoms based on their intrinsic energy. "But in experiments, they couldn't see it, and they were frustrated."
Scientists at the Honda Research Institute, who are interested in powerful batteries for electric cars, asked Yakobson to view the situation. "We looked at the theoretical capacity of an ideal sheet of graphene, and then how it could or could not benefit from curvature (into a nanotube) or topological defects. Our initial expectation was that it would improve lithium binding.
"But the theory didn't show any significant improvement," he said. "I was disappointed, but the experimentalists were satisfied because now their observations made sense."
Calculations involving graphene with defects, in which the honeycomb array is disrupted by five- and seven-atom polygons, fared no better. "So we decided to explore defects of different types where we replace some carbon atoms with another element that creates more attractive sites for lithium," he said. "And boron is one of them."
A carbon/boron compound in which a quarter of the carbon atoms are replaced by boron turned out to be nearly ideal as a way to activate graphene's ability to store lithium, Yakobson said. Boron attracts lithium ions into the matrix, but not so strongly that they can't be pulled away from a carbon/boron anode by a more attractive cathode.
"Having boron in the lattice gives very nice binding, so the capacity is good enough, two times larger than graphite," the most commonly used electrode in commercial lithium-ion batteries, he said. "At the same time, the voltage is also right."
Yakobson and Rice graduate student Yuanyue Liu, first author of the paper, calculated that a fully lithiated sheet of two-dimensional graphene/boron would have a capacity of 714 milliamp hours per gram. That translates to an energy density of 2,120 watt-hours per kilogram, far greater than graphite, when paired with a commercial lithium cobalt oxide cathode. They also determined the material would not radically expand or contract as it charges and discharges.
"In this case, it seems quite reasonable and exceeds -- theoretically, at least -- what is available now," Yakobson said.
An important step will be to find a way to synthesize the carbon/boron compound in large quantities. "It does exist, but it's not commercially available," he said.
Co-authors of the paper are Rice research associate Vasilii Artyukhov, Rice graduate student Mingjie Liu and Avetik Harutyunyan, a chief scientist at the Honda Research Institute.
The Honda Research Institute and the Department of Energy (DOE) supported the research. Computations were performed on the Rice DAVinCI system and the National Institute for Computational Sciences Kraken, both funded by the National Science Foundation, and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center Hopper, supported by the DOE.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








