Home > Press > Physicists discover a new kind of friction: Friction in the nano-world
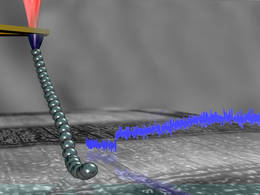 |
| A polymer chain tied to the tip of an atomic force microscope Image: B. Balzer/TUM |
Abstract:
Whether in vehicle transmissions, hip replacements, or tiny sensors for triggering airbags: The respective components must slide against each other with minimum friction to prevent loss of energy and material wear. Investigating the friction behavior of nanosystems, scientists from the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) have discovered a previously unknown type of friction that sheds new light on some previously unexplainable phenomena.
Physicists discover a new kind of friction: Friction in the nano-world
Munich, Germany | Posted on May 16th, 2013Friction is an omnipresent but often annoying physical ph�nomenon: It causes wear and energy loss in machines as well as in our joints. In search of low-friction components for ever smaller components, a team of physicists led by the professors Thorsten Hugel and Alexander Holleitner now discovered a previously unknown type of friction that they call "desorption stick."
The researchers examined how and why single polymer molecules in various solvents slide over or stick to certain surfaces. Their goal was to understand the basic laws of physics at the molecular scale in order to develop targeted anti-friction surfaces and suitable lubricants.
For their studies the scientists attached the end of a polymer molecule to the nanometer-fine tip of a highly sensitive atomic force microscope (AFM). While they pulled the polymer molecule over test surfaces, the AFM measured the resulting forces, from which the researchers could directly deduce the behavior of the polymer coil.
New friction mechanism discovered
Besides the two expected friction mechanisms such as sticking and sliding the researchers detected a third one for certain combinations of polymer, solvent and surface.
"Although the polymer sticks to the surface, the polymer strand can be pulled from its coiled conformation into the surrounding solution without significant force to be exerted," experimental physicist Thorsten Hugel describes this behavior. "The cause is probably a very low internal friction within the polymer coil."
The key is the solvent
Surprisingly, desorption stick depends neither on the speed of movement nor on the support surface or adhesive strength of the polymer. Instead, the chemical nature of the surface and the quality of the solvent are decisive. For example, hydrophobic polystyrene exhibits pure sliding behavior when dissolved in chloroform. In water, however, it shows desorption stick.
"The understanding gained by our measurement of single-molecule friction opens up new ways to minimize friction," says Alexander Holleitner. "In the future, with targeted preparation of polymers, new surfaces could be developed specifically for the nano- and micrometer range."
The work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Cluster of Excellence Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Andreas Battenberg
49-892-891-0510
Prof. Dr. Thorsten Hugel
Technische Universitaet Muenchen
Department of Physics / IMETUM
Boltzmannstr. 11, 85747 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 12884
Copyright © Technische Universitaet Muenchen
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








