Home > Press > Graphene’s high-speed seesaw
 |
Abstract:
A new transistor capable of revolutionising technologies for medical imaging and security screening has been developed by graphene researchers from the Universities of Manchester and Nottingham.
Graphene’s high-speed seesaw
Manchester, UK | Posted on April 30th, 2013Writing in Nature Communications, the researchers report the first graphene-based transistor with bistable characteristics, which means that the device can spontaneously switch between two electronic states. Such devices are in great demand as emitters of electromagnetic waves in the high-frequency range between radar and infra-red, relevant for applications such as security systems and medical imaging.
Bistability is a common phenomenon - a seesaw-like system has two equivalent states and small perturbations can trigger spontaneous switching between them. The way in which charge-carrying electrons in graphene transistors move makes this switching incredibly fast - trillions of switches per second.
Wonder material graphene is the world's thinnest, strongest and most conductive material, and has the potential to revolutionise a huge number of diverse applications; from smartphones and ultrafast broadband to drug delivery and computer chips. It was first isolated at The University of Manchester in 2004.
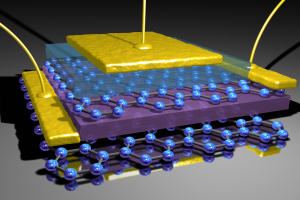
The device consists of two layers of graphene separated by an insulating layer of boron nitride just a few atomic layers thick. The electron clouds in each graphene layer can be tuned by applying a small voltage. This can induce the electrons into a state where they move spontaneously at high speed between the layers.
Because the insulating layer separating the two graphene sheets is ultra-thin, electrons are able to move through this barrier by ‘quantum tunnelling'. This process induces a rapid motion of electrical charge which can lead to the emission of high-frequency electromagnetic waves.
These new transistors exhibit the essential signature of a quantum seesaw, called negative differential conductance, whereby the same electrical current flows at two different applied voltages. The next step for researchers is to learn how to optimise the transistor as a detector and emitter.
One of the researchers, Professor Laurence Eaves, said: "In addition to its potential in medical imaging and security screening, the graphene devices could also be integrated on a chip with conventional, or other graphene-based, electronic components to provide new architectures and functionality.
"For more than 40 years, technology has led to ever-smaller transistors; a tour de force of engineering that has provided us with today's state-of-the-art silicon chips which contain billions of transistors. Scientists are searching for an alternative to silicon-based technology, which is likely to hit the buffers in a few years' time, and graphene may be an answer."
"Graphene research is relatively mature but multi-layered devices made of different atomically-thin materials such as graphene were first reported only a year ago. This architecture can bring many more surprises", adds Dr Liam Britnell, University of Manchester, the first author of the paper.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Daniel Cochlin
Graphene Communications and Marketing Manager
The University of Manchester
0161 275 8382
07917 506158
www.graphene.manchester.ac.uk
www.manchester.ac.uk
Twitter: @UoMGraphene
Copyright © Universitiy of Manchester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() More information about graphene is available from:
More information about graphene is available from:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








