Home > Press > Small in size, big on power: New microbatteries a boost for electronics
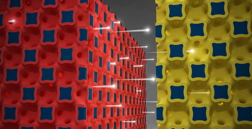 |
| Image courtesy of the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology
The graphic illustrates a high power battery technology from the University of Illinois. Ions flow between three-dimensional micro-electrodes in a lithium ion battery. |
Abstract:
Though they be but little, they are fierce. The most powerful batteries on the planet are only a few millimeters in size, yet they pack such a punch that a driver could use a cellphone powered by these batteries to jump-start a dead car battery - and then recharge the phone in the blink of an eye.
Small in size, big on power: New microbatteries a boost for electronics
Champaign, IL | Posted on April 16th, 2013Developed by researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, the new microbatteries out-power even the best supercapacitors and could drive new applications in radio communications and compact electronics.
Led by William P. King, the Bliss Professor of mechanical science and engineering, the researchers published their results in the April 16 issue of Nature Communications.
"This is a whole new way to think about batteries," King said. "A battery can deliver far more power than anybody ever thought. In recent decades, electronics have gotten small. The thinking parts of computers have gotten small. And the battery has lagged far behind. This is a microtechnology that could change all of that. Now the power source is as high-performance as the rest of it."
With currently available power sources, users have had to choose between power and energy. For applications that need a lot of power, like broadcasting a radio signal over a long distance, capacitors can release energy very quickly but can only store a small amount. For applications that need a lot of energy, like playing a radio for a long time, fuel cells and batteries can hold a lot of energy but release it or recharge slowly.
"There's a sacrifice," said James Pikul, a graduate student and first author of the paper. "If you want high energy you can't get high power; if you want high power it's very difficult to get high energy. But for very interesting applications, especially modern applications, you really need both. That's what our batteries are starting to do. We're really pushing into an area in the energy storage design space that is not currently available with technologies today."
The new microbatteries offer both power and energy, and by tweaking the structure a bit, the researchers can tune them over a wide range on the power-versus-energy scale.
The batteries owe their high performance to their internal three-dimensional microstructure. Batteries have two key components: the anode (minus side) and cathode (plus side). Building on a novel fast-charging cathode design by materials science and engineering professor Paul Braun's group, King and Pikul developed a matching anode and then developed a new way to integrate the two components at the microscale to make a complete battery with superior performance.
With so much power, the batteries could enable sensors or radio signals that broadcast 30 times farther, or devices 30 times smaller. The batteries are rechargeable and can charge 1,000 times faster than competing technologies - imagine juicing up a credit-card-thin phone in less than a second. In addition to consumer electronics, medical devices, lasers, sensors and other applications could see leaps forward in technology with such power sources available.
"Any kind of electronic device is limited by the size of the battery - until now," King said. "Consider personal medical devices and implants, where the battery is an enormous brick, and it's connected to itty-bitty electronics and tiny wires. Now the battery is also tiny."
Now, the researchers are working on integrating their batteries with other electronics components, as well as manufacturability at low cost.
"Now we can think outside of the box," Pikul said. "It's a new enabling technology. It's not a progressive improvement over previous technologies; it breaks the normal paradigms of energy sources. It's allowing us to do different, new things."
The National Science Foundation and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research supported this work. King also is affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology; the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory; the Micro and Nanotechnology Laboratory; and the department of electrical and computer engineering at the U. of I.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liz Ahlberg
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1079
William King
217-244-3864
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








