Home > Press > Tin nanocrystals for the battery of the future
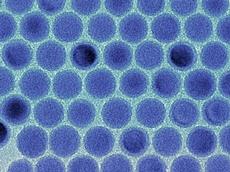 |
| Monodisperse tin nanodroplets in an electron microscopic image. Image: Maksym Kovalenko / ETH Zürich |
Abstract:
More powerful batteries could help electric cars achieve a considerably larger range and thus a breakthrough on the market. A new nanomaterial for lithium ion batteries developed in the labs of chemists at ETH Zurich and Empa could come into play here.
Tin nanocrystals for the battery of the future
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on April 8th, 2013 They provide power for electric cars, electric bicycles, smartphones and laptops; nowadays, rechargeable lithium ion batteries are the storage media of choice when it comes to supplying a large amount of energy in a small space and light weight. All over the world, scientists are currently researching a new generation of such batteries with an improved performance. Scientists headed by Maksym Kovalenko from the Laboratory of Inorganic Chemistry at ETH Zurich and Empa have now developed a nanomaterial which enables considerably more power to be stored in lithium ion batteries.
The nanomaterial is composed of tiny tin crystals, which are to be deployed at the minus pole of the batteries (anode). When charging the batteries, lithium ions are absorbed at this electrode; while discharging, they are released again (see box). "The more lithium ions the electrodes can absorb and release - the better they can breathe, as it were - the more energy can be stored in a battery," explains Kovalenko.
Uniform crystals
The element tin is ideal for this: every tin atom can absorb at least four lithium ions. However, the challenge is to deal with the volume change of tin electrodes: tin crystal becomes up to three times bigger if it absorbs a lot of lithium ions and shrinks again when it releases them back. The scientists thus resorted to nanotechnology: they produced the tiniest tin nanocrystals and embedded a large number of them in a porous, conductive permeable carbon matrix. Much like how a sponge can suck up water and release it again, an electrode constructed in this way can absorb lithium ions while charging and release them when discharging. If the electrode were made of a compact tin block, this would practically be impossible.
During the development of the nanomaterial, the issue of the ideal size for the nanocrystals arose, which also carries the challenge of producing uniform crystals. "The trick here was to separate the two basic steps in the formation of the crystals - the formation of as small as a crystal nucleus as possible on the one hand and its subsequent growth on the other," explains Kovalenko. By influencing the time and temperature of the growth phase, the scientists were able to control the size of the crystals. "We are the first to produce such small tin crystals with such precision," says the scientist.
Larger cycle stability
Using uniform tin nanocrystals, carbon, and binding agents, the scientists produced different test electrodes for batteries. "This enables twice as much power to be stored compared to conventional electrodes," says Kovalenko. The size of the nanocrystals did not affect the storage capacity during the initial charging and discharging cycle. After a few charging and discharging cycles, however, differences caused by the crystal size became apparent: batteries with ten-nanometre crystals in the electrodes were able to store considerably more energy than ones with twice the diameter. The scientists assume that the smaller crystals perform better because they can absorb and release lithium ions more effectively. "Ten-nanometre tin crystals thus seem to be just the ticket for lithium ion batteries," says Kovalenko.
As the scientists now know the ideal size for the tin nanocrystals, they would like to turn their attention to the remaining challenges of producing optimum tin electrodes in further research projects. These include the choice of the best possible carbon matrix and binding agent for the electrodes, and the electrodes' ideal microscopic structure. Moreover, an optimal and stable electrolyte liquid in which the lithium ions can travel back and forth between the two poles in the battery also needs to be selected. Ultimately, the production costs are also an issue, which the researchers are looking to reduce by testing which cost-effective base materials are suitable for electrode production. The aim is to prepare batteries with an increased energy storage capacity and lifespan for the market, in collaboration with a Swiss industrial partner.
How lithium ion batteries work
In lithium ion batteries, the energy is stored in the form of positively charged lithium atoms (ions) that are found at the minus pole in a charged battery. If energy is taken from the battery, negatively charged electrons flow from the minus pole to the plus pole via the external circuit. To balance the charge, positively charged lithium ions also flow from the minus pole to the plus pole. However, these travel in the electrolyte fluid inside the battery. The process is reversible: lithium ion batteries can be recharged with electricity. In most lithium ion batteries these days, the plus pole is composed of the transition metal oxides cobalt, nickel, and manganese, the minus pole of graphite. In more powerful lithium ion batteries of the next generation, however, elements such as tin or silicon may well be used at the minus pole.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Maksym Kovalenko
41-446-334-156
Copyright © ETH Zurich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Related story "Tortuous paths hamper ion transport":
Related story "Tortuous paths hamper ion transport":
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








