Home > Press > Rice builds nanotube photodetector: Project with Sandia National Laboratories leads to promising optoelectronic device
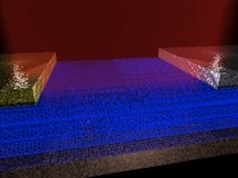 |
| This illustration shows an array of parallel carbon nanotubes 300 micrometers long that are attached to electrodes and display unique qualities as a photodetector, according to researchers at Rice University and Sandia National Laboratories. (Credit: Sandia National Laboratories) |
Abstract:
Researchers at Rice University and Sandia National Laboratories have made a nanotube-based photodetector that gathers light in and beyond visible wavelengths. It promises to make possible a unique set of optoelectronic devices, solar cells and perhaps even specialized cameras.
Rice builds nanotube photodetector: Project with Sandia National Laboratories leads to promising optoelectronic device
Houston, TX | Posted on February 27th, 2013A traditional camera is a light detector that captures a record, in chemicals, of what it sees. Modern digital cameras replaced film with semiconductor-based detectors.
But the Rice detector, the focus of a paper that appeared today in the online Nature journal Scientific Reports, is based on extra-long carbon nanotubes. At 300 micrometers, the nanotubes are still only about 100th of an inch long, but each tube is thousands of times longer than it is wide.
That boots the broadband detector into what Rice physicist Junichiro Kono considers a macroscopic device, easily attached to electrodes for testing. The nanotubes are grown as a very thin "carpet" by the lab of Rice chemist Robert Hauge and pressed horizontally to turn them into a thin sheet of hundreds of thousands of well-aligned tubes.
They're all the same length, Kono said, but the nanotubes have different widths and are a mix of conductors and semiconductors, each of which is sensitive to different wavelengths of light. "Earlier devices were either a single nanotube, which are sensitive to only limited wavelengths," he said. "Or they were random networks of nanotubes that worked, but it was very difficult to understand why."
"Our device combines the two techniques," said Sébastien Nanot, a former postdoctoral researcher in Kono's group and first author of the paper. "It's simple in the sense that each nanotube is connected to both electrodes, like in the single-nanotube experiments. But we have many nanotubes, which gives us the quality of a macroscopic device."
With so many nanotubes of so many types, the array can detect light from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet, and all the visible wavelengths in between. That it can absorb light across the spectrum should make the detector of great interest for solar energy, and its IR capabilities may make it suitable for military imaging applications, Kono said. "In the visible range, there are many good detectors already," he said. "But in the IR, only low-temperature detectors exist and they are not convenient for military purposes. Our detector works at room temperature and doesn't need to operate in a special vacuum."
The detector is also sensitive to polarized light and absorbs light that hits it parallel to the nanotubes, but not if the device is turned 90 degrees.
The work is the first successful outcome of a collaboration between Rice and Sandia under Sandia's National Institute for Nano Engineering program funded by the Department of Energy. François Léonard's group at Sandia developed a novel theoretical model that correctly and quantitatively explained all characteristics of the nanotube photodetector. "Understanding the fundamental principles that govern these photodetectors is important to optimize their design and performance," Léonard said.
Kono expects many more papers to spring from the collaboration. The initial device, according to Léonard, merely demonstrates the potential for nanotube photodetectors. They plan to build new configurations that extend their range to the terahertz and to test their abilities as imaging devices. "There is potential here to make real and useful devices from this fundamental research," Kono said.
Co-authors are Aron Cummings, a postdoctoral fellow in Léonard's Nanoelectronics and Nanophotonics Group at Sandia; Rice alumnus Cary Pint, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Vanderbilt University; Kazuhisa Sueoka, a professor at Hokkaido University; and Akira Ikeuchi and Takafumi Akiho, Hokkaido University graduate students who worked in Kono's lab as part of Rice's NanoJapan program. Hauge is a distinguished faculty fellow in chemistry. Kono is a professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics and astronomy.
The U.S. Department of Energy, the National Institute for Nano Engineering at Sandia National Laboratories, the Lockheed Martin Advanced Nanotechnology Center of Excellence at Rice University, the National Science Foundation and the Robert A. Welch Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Optoelectronic Properties of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes:
Optoelectronic Properties of Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








