Home > Press > New synthesis method produces nanoparticles in high quantities
 |
Abstract:
TiO2 nanoparticles are in increasingly high demand for a range of applications, including photocatalysts, photonic crystals, photovoltaic cells, gas sensors, fuel cells, pigments and cosmetics. Now researchers in Japan have demonstrated a new method for synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles in large amounts.
New synthesis method produces nanoparticles in high quantities
Kanazawa, Japan | Posted on February 25th, 2013Researchers have already used inductively coupled thermal plasmas (ICTPs) as a useful source of heat and chemicals in synthesis. These plasmas are forms of the chemical that have been ionised by energy produced by electric currents produced by fluctuating magnetic fields, so-called electromagnetic induction. However application of ICTPs in nanoparticle synthesis has met with difficulties in controlling the particle size.
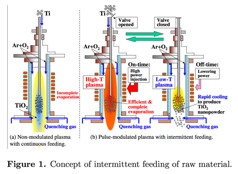
Yasunori Tanaka and colleagues at Kanazawa University and Nisshin Seifun Group in Japan had previously modified the ICTP approach using a modulated current coil to give voltage pulses and other arbitrary waveforms. The modulated current provides a means of controlling the temperature and density of the chemical species during synthesis. Applying these pulse-modulated inductive thermal plasmas (PMITP) to TiO2 nanoparticle synthesis allowed control over the particle size and mineral phase. However, due to the latent heat of evaporation of the powders, there was a limit to how much the feed rate could be increased before the ICTP failed to evaporate all the powder.
Now the researchers have demonstrated that carefully timed intermittent feeding combined with gas quenching to synchronise with the pulse modulation of the induction thermal plasmas allowed oxidation of all the titanium into TiO2 nanoparticle even when synthesised in large amounts. They conclude, "The results indicated that the synthesized particles by the 20-kW PMITP with a heavy loading rate of 12.3 g/min had a similar particle size distribution with the mean diameter about 40 nm to those with light loading of 4.2 g/min."
1. Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Kanazawa University, Kakuma, Kanazawa 920-1192, Japan
2. Research Center for Production & Technology, Nisshin Seifun Group Inc.,5-3-1 Tsurugaoka, Fujimino 356-8511, Japan
*corresponding author, e-mail address:
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Organization of Frontier Science and Innovation
Kanazawa University
Kakuma, Kanazawa, Ishikawa 920-1192, Japan
Copyright © Kanazawa University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Personal Care/Cosmetics
![]() DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on "Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology" May 12th, 2023
DGIST and New Life Group launched a research project on "Functional beauty and health products using the latest nanotechnology" May 12th, 2023
![]() A Comprehensive Guide: The Future of Nanotechnology September 13th, 2018
A Comprehensive Guide: The Future of Nanotechnology September 13th, 2018
![]() Graphene finds new application as anti-static hair dye: New formula works as well as commercial permanent dyes without chemically altering hairs March 22nd, 2018
Graphene finds new application as anti-static hair dye: New formula works as well as commercial permanent dyes without chemically altering hairs March 22nd, 2018
![]() Programmable materials find strength in molecular repetition May 23rd, 2016
Programmable materials find strength in molecular repetition May 23rd, 2016
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








