Home > Press > A quantum dot energy harvester: Turning Waste Heat into Electricity on the Nanoscale
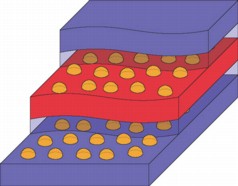 |
| An array on nano energy harvesters in what the researchers call a "swiss cheese" arrangement. |
Abstract:
A new type of nanoscale engine has been proposed that would use quantum dots to generate electricity from waste heat, potentially making microcircuits more efficient. The engines would be microscopic in size, and have no moving parts. Each would only produce a tiny amount of power but by combining millions of the engines in a layered structure, enough of them could make a notable difference in the energy consumption of a computer.
A quantum dot energy harvester: Turning Waste Heat into Electricity on the Nanoscale
Rochester, NY | Posted on February 14th, 2013A new type of nanoscale engine has been proposed that would use quantum dots to generate electricity from waste heat, potentially making microcircuits more efficient.
"The system is really a simple one, which exploits certain properties of quantum dots to harvest heat," Professor Andrew Jordan of the University of Rochester said. "Despite this simplicity, the power it could generate is still larger than any other nanoengine that has been considered until now."
The engines would be microscopic in size, and have no moving parts. Each would only produce a tiny amount of power - a millionth or less of what a light bulb uses. But by combining millions of the engines in a layered structure, Jordan says a device that was a square inch in area could produce about a watt of power for every one degree difference in temperature. Enough of them could make a notable difference in the energy consumption of a computer.
A paper describing the new work is being published in Physical Review B by Jordan, a theoretical physics professor, and his collaborators, Björn Sothmann and Markus Buttiker from the University of Geneva, and Rafael Sánchez from the Material Sciences Institute in Madrid.
Jordan explained that each of the proposed nanoengines is based on two adjacent quantum dots, with current flowing through one and then the other. Quantum dots are manufactured systems that due to their small size act as quantum mechanical objects, or artificial atoms.
The path the electrons have to take across both quantum dots can be adjusted to have an uphill slope. To make it up this (electrical) hill, electrons need energy. They take the energy from the middle of the region, which is kept hot, and use this energy to come out the other side, higher up the hill. This removes heat from where it is being generated and converts it into electrical power with a high efficiency.
To do this, the system makes use of a quantum mechanical effect called resonant tunneling, which means the quantum dots act as perfect energy filters. When the system is in the resonant tunneling mode, electrons can only pass through the quantum dots when they have a specific energy that can be adjusted. All other electrons that do not have this energy are blocked.
Quantum dots can be grown in a self-assembling way out of semiconductor materials. This allows for a practical way to produce many of these tiny engines as part of a larger array, and in multiple layers, which the authors refer to as the Swiss Cheese Sandwich configuration (see image).
How much electrical power is produced depends on the temperature difference across the energy harvester - the higher the temperature difference, the higher the power that will be generated. This requires good insulation between the hot and cold regions, Jordan says.
####
About University of Rochester
The University of Rochester (www.rochester.edu) is one of the nation's leading private universities. Located in Rochester, N.Y., the University gives students exceptional opportunities for interdisciplinary study and close collaboration with faculty through its unique cluster-based curriculum. Its College, School of Arts and Sciences, and Hajim School of Engineering and Applied Sciences are complemented by its Eastman School of Music, Simon School of Business, Warner School of Education, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, School of Medicine and Dentistry, School of Nursing, Eastman Institute for Oral Health, and the Memorial Art Gallery.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Leonor Sierra
585.276.6264
Copyright © University of Rochester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








