Home > Press > Team creates MRI for the nanoscale
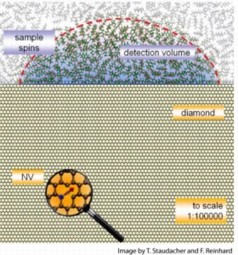 |
| A tiny defect, called a nitrogen vacancy (NV), inside a diamond enabled researchers to detect the magnetic resonance of organic molecules in the same way an MRI produces images of a tissue or an organ. |
Abstract:
An international team of researchers including CCNY and the University of Stuttgart have opened the door for MRI technology at the nanoscale. Using tiny defects in diamonds they sensed the magnetic resonance of molecules to peer down to the level of atoms.
Team creates MRI for the nanoscale
New York, NY | Posted on February 13th, 2013Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reveals details of living tissues, diseased organs and tumors inside the body without x-rays or surgery. What if the same technology could peer down to the level of atoms? Doctors could make visual diagnoses of a person's molecules - examining damage on a strand of DNA, watching molecules misfold, or identifying a cancer cell by the proteins on its surface.
Now Dr. Carlos Meriles, associate professor of physics at The City College of New York, and an international team of researchers at the University of Stuttgart and elsewhere have opened the door for nanoscale MRI. They used tiny defects in diamonds to sense the magnetic resonance of molecules. They reported their results in the February 1 issue of Science.
"It is bringing MRI to a level comparable to an atomic force microscope," said Professor Meriles, referring to the device that traces the contours of atoms or tugs on a molecule to measure its strength. A nanoscale MRI could display how a molecule moves without touching it.
"Standard MRI typically gets to a resolution of 100 microns," about the width of a human hair, said Professor Meriles. "With extraordinary effort," he said, "it can get down to about 10 microns" - the width of a couple of blood cells. Nanoscale MRI would have a resolution 1,000 to 10,000 times better.
To try to pick up magnetic resonance on such a small scale, the team took advantage of the spin of protons in an atom, a property usually used to investigate quantum computing. In particular, they used minute imperfections in diamonds.
Diamonds are crystals made up almost entirely of carbon atoms. When a nitrogen atom lodges next to a spot where a carbon atom is missing, however, it creates a defect known as a nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center.
"These imperfections turn out to have a spin - like a little compass - and have some remarkable properties," noted Professor Meriles. In the last few years, researchers realized that these NV centers could serve as very sensitive sensors. They can pick up the magnetic resonance of nearby atoms in a cell, for example. But unlike the atoms in a cell, the NVs shine when a light is directed at them, signaling what their spin is. If you illuminate it with green light it flashes red back.
"It is a form of what is called optically detected magnetic resonance," he said. Like a hiker flashing Morse code on a hillside, the sensor "sends back flashes to say it is alive and well."
"The NV can also be thought of as an atomic magnet. You can manipulate the spin of that atomic magnet just like you do with MRI by applying a radio frequency or radio pulses," Professor Meriles explained. The NV responds. Shine a green light at it when the spin is pointing up and it will respond with brighter red light. A down spin gives a dimmer red light.
Professor Mireles has written on the theoretical underpinnings of the work and proposed the the project to the team, led by Professor Jörg Wrachtrup — a physicist at the University of Stuttgart in Germany — with the assistance of postdoctoral researcher Friedemann Reinhard and collaborators from the University of Bochum and the University of Science and Technology of China. Professor Wrachtrup heads a leading group studying such defects.
In the lab, graduate student Tobias Staudacher — the first author in this work — used NVs that had been created just below the diamond's surface by bombarding it with nitrogen atoms. The team detected magnetic resonance within a film of organic material applied to the surface, just as one might examine a thin film of cells or tissue.
"Ultimately," said Professor Meriles, "One will use a nitrogen-vacancy mounted on the tip of an atomic force microscope - or an array of NVs distributed on the diamond surface - to allow a scanning view of a cell, for example, to probe nuclear spins with a resolution down to a nanometer or perhaps better."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jessa Netting
212-650-7615
Copyright © City College of New York
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








