Home > Press > Light-emitting triangles may have applications in optical technology
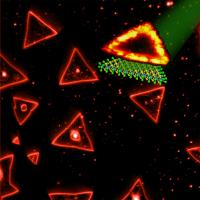 |
| Triangular single layers of tungsten disulfide have been synthesized by Penn State researchers. The edges of the triangles exhibit extraordinary photoluminescence, while the interior area does not. The photoluminescent signal disappears as the number of layers increases. These triangular structures may have potential applications in optical technology; for example, for use in light detectors and lasers.
Credit: Terrones lab, Penn State Universtiy |
Abstract:
For the first time, scientists have created single layers of a naturally occurring rare mineral called tungstenite, or WS2. The resulting sheet of stacked sulfur and tungsten atoms forms a honeycomb pattern of triangles that have been shown to have unusual light-emitting, or photoluminescent, properties. According to team leader Mauricio Terrones, a professor of physics and of materials science and engineering at Penn State, the triangular structures have potential applications in optical technology; for example, for use in light detectors and lasers. The results of the research will be published in a print edition of the journal NANO Letters.
Light-emitting triangles may have applications in optical technology
University Park, PA | Posted on February 5th, 2013Terrones explained that creating monolayers -- single, one-atom-thick layers -- is of special interest to scientists because the chemical properties of minerals and other substances are known to change depending on their atomic thickness, opening the door to potentially useful applications of multi-layered materials of various thicknesses. In previous research, scientists had accomplished the feat of making a monolayer of graphene -- a substance similar to the graphite found in pencil leads. "The technique these researchers used was tedious, but it worked," Terrones said. "They basically removed, or exfoliated, the graphene, layer by layer, with Scotch tape, until they got down to a single atom of thickness."
Now, for the first time, Terrones and his team have used a controlled thermal reduction-sulfurization method -- or chemical vapor deposition -- to accomplish the same feat with a rare mineral called tungstenite. The scientists began by depositing tiny crystals of tungsten oxide, which are less than one nanometer in height, and they then passed the crystals through sulfur vapor at 850 degrees Celsius. This process led to individual layers -- or sheets -- composed of one atom in thickness. The resulting structure -- called tungsten disulfide -- is a honeycomb pattern of triangles consisting of tungsten atoms bonded with sulfur atoms.
"One of the most exciting properties of the tungsten disulfide monolayer is its photoluminescence," Terrones said. Terrones explained that photoluminescence occurs when a substance absorbs light at one wavelength and re-emits that light at a different wavelength. The property of photoluminescence also occurs in certain bioluminescenent animals such as angler fish and fireflies. "One interesting discovery from our work is the fact that we see the strongest photoluminescence at the edges of the triangles, right where the chemistry of the atoms changes, with much less photoluminescence occurring in the center of the triangles," Terrones said. "We also have found that these new monolayers luminesce at room temperature. So no special temperature requirements are needed for the material to exhibit this property."
Co-author Vincent H. Crespi, Distinguished Professor of Physics, Chemistry, and Materials Science and Engineering at Penn State, added, "The images of the photoluminescence are beautiful; the triangles light up all around their edges like little holiday ornaments -- holiday ornaments with potentially transformative, long-term applications in nano-optics."
The research has many potential applications in the fields of optical light detection, the production of light-emitting diodes, and even laser technology. The researchers also plan to try the chemical-vapor-deposition technology to grow innovative monolayers using other layered materials with potentially useful applications.
In addition to Terrones and Crespi, other researchers who contributed to this study include Humberto R. Gutiérrez, an assistant professor at the University of Louisville; Nestor Perea-López and Ana Laura Elías, research associates at Penn State; Ayse Berkdemir and Ruitao Lv, posdoctoral fellows at Penn State; Bei Wang and Yuanxi Wang, graduate students at Penn State; and Florentino López-Urías and Humberto Terrones, visiting professors at Penn State.
Support for this research comes primarily from the U.S. Army Research Office and, in part, from the Penn State Center for Nanoscale Science.
[ Katrina Voss ]
GRANT NUMBERS: U.S. Army Research Office (MURI grant W911NF-11-1-0362), Penn State Center for Nanoscale Science (DMR-0820404)
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Barbara Kennedy
814-863-4682
Mauricio Terrones:
814-865-0343
Vincent H. Crespi
814-863-0163
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








