Home > Press > DNA and quantum dots: All that glitters is not gold
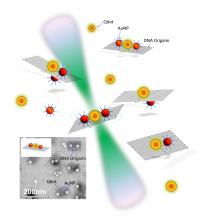 |
| The NIST team explored the behavior of quantum dots and gold nanoparticles placed in different configurations on small rectangular constructs made of self-assembled DNA (see inset for photograph). Laser light (green) allowed the team to explore changes in the fluorescent lifetime of the quantum dots when close to gold particles of different sizes.
Credit: NIST |
Abstract:
A team of researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has shown that by bringing gold nanoparticles close to the dots and using a DNA template to control the distances, the intensity of a quantum dot's fluorescence can be predictably increased or decreased.* This breakthrough opens a potential path to using quantum dots as a component in better photodetectors, chemical sensors and nanoscale lasers.
DNA and quantum dots: All that glitters is not gold
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on January 25th, 2013Anyone who has tried to tune a radio knows that moving their hands toward or away from the antenna can improve or ruin the reception. Although the reasons are well understood, controlling this strange effect is difficult, even with hundred-year-old radio technology. Similarly, nanotechnology researchers have been frustrated trying to control the light emitted from quantum dots, which brighten or dim with the proximity of other particles.
The NIST team developed ways to accurately and precisely place different kinds of nanoparticles near each other and to measure the behavior of the resulting nanoscale constructs. Because nanoparticle-based inventions may require multiple types of particles to work together, it is crucial to have reliable methods to assemble them and to understand how they interact.
The researchers looked at two types of nanoparticles, quantum dots, which glow with fluorescent light when illuminated, and gold nanoparticles, which have long been known to enhance the intensity of light around them. The two could work together to make nanoscale sensors built using rectangles of woven DNA strands, formed using a technique called "DNA origami."
These DNA rectangles can be engineered to capture different types of nanoparticles at specific locations with a precision of about one nanometer. Tiny changes in the distance between a quantum dot and a gold nanoparticle near one another on the rectangle cause the quantum dot to glow more or less brightly as it moves away from or toward the gold. Because these small movements can be easily detected by tracking the changes in the quantum dot's brightness, they can be used to reveal, for example, the presence of a particular chemical that is selectively attached to the DNA rectangle. However, getting it to work properly is complicated, says NIST's Alex Liddle.
"A quantum dot is highly sensitive to the distance between it and the gold, as well as the size, number and arrangement of the gold particles," says Liddle, a scientist with the NIST Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology. "These factors can boost its fluorescence, mask it or change how long its glow lasts. We wanted a way to measure these effects, which had never been done before."
Liddle and his colleagues made several groups of DNA rectangles, each with a different configuration of quantum dots and gold particles in a solution. Using a laser as a spotlight, the team was able to follow the movement of individual DNA rectangles in the liquid, and also could detect changes in the fluorescent lifetime of the quantum dots when they were close to gold particles of different sizes. They also showed that they could exactly predict the lifetime of the fluorescence of the quantum dot depending on the size of the nearby gold nanoparticles.
While their tracking technique was time consuming, Liddle says that the strength of their results will enable them to engineer the dots to have a specific desired lifetime. Moreover, the success of their tracking method could lead to better measurement methods.
"Our main goals for the future," he concludes, "are to build better nanoscale sensors using this approach and to develop the metrology necessary to measure their performance."
*S.H. Ko, K. Du and J.A. Liddle.Quantum-dot fluorescence lifetime engineering with DNA origami constructs. Angewandte Chemie (Int. Ed.), 52: 1193-1197. doi: 10.1002/anie.201206253.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chad Boutin
301-975-4261
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NISTís grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








