Home > Press > Nature Communications – Nanoparticles Digging the World’s Smallest Tunnels
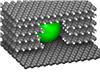 |
| Graphite consists of layered carbon atoms. A metal particle bores into the graphite sample from the edges of these layers. (Photo: KIT) |
Abstract:
The world's smallest tunnels have a width of a few nanometers only. Researchers from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and Rice University, USA, have dug such tunnels into graphite samples. This will allow structuring of the interior of materials through self-organization in the nanometer range and tailoring of nanoporous graphite for applications in medicine and battery technology. Results are now presented in the scientific journal Nature Communications. (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2399)
Nature Communications – Nanoparticles Digging the World’s Smallest Tunnels
Karlsruhe, Germany | Posted on January 24th, 2013The tunnels are manufactured applying nickel nanoparticles to graphite which then is heated in the presence of hydrogen gas. The surface of the metal particles, that measure a few nanometers only, serves as a catalyst removing the carbon atoms of the graphite and converting them by means of hydrogen into the gas methane. Through capillary forces, the nickel particle is drawn into the "hole" that forms and bores through the material. The size of the tunnels obtained in the experiments was in the range of 1 to 50 nanometers, which about corresponds to one thousandth of the diameter of a human hair.
To furnish proof of the real existence of these graphite tunnels, the researchers have made use of scanning electron and scanning tunneling microscopy. "Microscopes, in fact, image only the upper layers of the sample," the principal authors of the study, Maya Lukas and Velimir Meded from KIT's Institute of Nanotechnology, explain. "The tunnels below these upper layers, however, leave atomic structures on the surface whose courses can be traced and which can be assigned to the nanotunnels by means of the very detailed scanning tunneling microscopy images and based on computerized simulations." In addition, the depth of the tunnels was determined precisely by means of a series of images taken by a scanning electron microscope from different perspectives.
Porous graphite is used, for example, in the electrodes of lithium ion batteries. The charge time could be reduced using materials with appropriate pore sizes. In medicine, porous graphite could serve as a carrier of drugs to be released over longer periods of time. Replacing graphite by nonconductive materials, e.g. boron nitride, with atomic structures similar to that of graphite, the tunnels could serve as basic structures for nanoelectronic components such as novel sensors or solar cells.
The graphite tunnel study was carried out by the study groups headed by Pulickel M. Ajayan from Rice University, USA, and Ralph Krupke and Wolfgang Wenzel from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.
Full bibliographic information
Maya Lukas, Velimir Meded, Aravind Vijayaraghavan, Li Song, Pulickel M. Ajayan, Karin Fink, Wolfgang Wenzel, Ralph Krupke, Catalytic subsurface etching of nanoscale channels in graphite, Nat. Commun. 4 : 1379, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2399
####
About Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation according to the legislation of the state of Baden-Württemberg. It fulfills the mission of a university and the mission of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. KIT focuses on a knowledge triangle that links the tasks of research, teaching, and innovation.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Monika Landgraf
Karlsruher Institut für Technologie
+49 721 608 47414
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








