Home > Press > Putting the squeeze on cells: By deforming cells, researchers can deliver RNA, proteins and nanoparticles for many applications.
 |
Abstract:
Living cells are surrounded by a membrane that tightly regulates what gets in and out of the cell. This barrier is necessary for cells to control their internal environment, but it makes it more difficult for scientists to deliver large molecules such as nanoparticles for imaging, or proteins that can reprogram them into pluripotent stem cells.
Putting the squeeze on cells: By deforming cells, researchers can deliver RNA, proteins and nanoparticles for many applications.
Cambridge, MA | Posted on January 23rd, 2013Researchers from MIT have now found a safe and efficient way to get large molecules through the cell membrane, by squeezing the cells through a narrow constriction that opens up tiny, temporary holes in the membrane. Any large molecules floating outside the cell — such as RNA, proteins or nanoparticles — can slide through the membrane during this disruption.
Using this technique, the researchers were able to deliver reprogramming proteins and generate induced pluripotent stem cells with a success rate 10 to 100 times better than any existing method. They also used it to deliver nanoparticles, including carbon nanotubes and quantum dots, which can be used to image cells and monitor what's happening inside them.
"It's very useful to be able to get large molecules into cells. We thought it might be interesting if you could have a relatively simple system that could deliver many different compounds," says Klavs Jensen, the Warren K. Lewis Professor of Chemical Engineering, professor of materials science and engineering, and a senior author of a paper describing the new device in this week's issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Robert Langer, the David H. Koch Institute Professor at MIT, is also a senior author of the paper. Lead authors are chemical engineering graduate student Armon Sharei, Koch Institute research scientist Janet Zoldan, and chemical engineering research associate Andrea Adamo.
A general approach
Biologists have previously developed several ways to get large molecules into cells, but all of them have drawbacks. DNA or RNA can be packaged into viruses, which are adept at entering cells, but that approach carries the risk that some of the viral DNA will get integrated into the host cell. This method is commonly used in lab experiments but has not been approved by the FDA for use in human patients.
Another way to sneak large molecules into a cell is to tag them with a short protein that can penetrate the cell membrane and drag the larger cargo along with it. Alternatively, DNA or proteins can be packaged into synthetic nanoparticles that can enter cells. However, these systems often need to be re-engineered depending on the type of cell and material being delivered. Also, with some nanoparticles much of the material ends up trapped in protective sacs called endosomes inside the cell, and there can be potential toxic side effects.
Electroporation, which involves giving cells a jolt of electricity that opens up the cell membrane, is a more general approach but can be damaging to both cells and the material being delivered.
The new MIT system appears to work for many cell types — so far, the researchers have successfully tested it with more than a dozen types, including both human and mouse cells. It also works in cells taken directly from human patients, which are usually much more difficult to manipulate than human cell lines grown specifically for lab research.
"This appears to be a very broadly applicable approach for loading a diversity of different compounds into a diversity of different cells," says Mark Prausnitz, a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at Georgia Tech, who was not part of the research team. "It's a really nice example of taking devices from the world of engineering and microelectronics and using them in quite different ways to solve problems in medicine that could have really great impact."
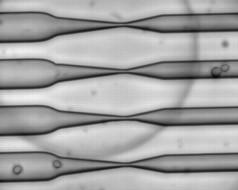
The new device builds on previous work by Jensen and Langer's labs, in which they used microinjection to force large molecules into cells as they flowed through a microfluidic device. This wasn't as fast as the researchers would have liked, but during these studies, they discovered that when a cell is squeezed through a narrow tube, small holes open in the cell membrane, allowing nearby molecules to diffuse into the cell.
To take advantage of that, the researchers built rectangular microfluidic chips, about the size of a quarter, with 40 to 70 parallel channels. Cells are suspended in a solution with the material to be delivered and flowed through the channel at high speed — about one meter per second. Halfway through the channel, the cells pass through a constriction about 30 to 80 percent smaller than the cells' diameter. The cells don't suffer any irreparable damage, and they maintain their normal functions after the treatment.
Special delivery
The research team is now further pursuing stem cell manipulation, which holds promise for treating a wide range of diseases. They have already shown that they can transform human fibroblast cells into pluripotent stem cells, and now plan to start working on delivering the proteins needed to differentiate stem cells into specialized tissues.
Another promising application is delivering quantum dots — nanoparticles made of semiconducting metals that fluoresce. These dots hold promise for labeling individual proteins or other molecules inside cells, but scientists have had trouble getting them through the cell membrane without getting trapped in endosomes.
In a paper published in November, working with MIT graduate student Jungmin Lee and chemistry professor Moungi Bawendi, the researchers showed that they could get quantum dots inside human cells grown in the lab, without the particles becoming confined in endosomes or clumping together. They are now working on getting the dots to tag specific proteins inside the cells.
The researchers are also exploring the possibility of using the new system for vaccination. In theory, scientists could remove immune cells from a patient, run them through the microfluidic device and expose them to a viral protein, and then put them back in the patient. Once inside, the cells could provoke an immune response that would confer immunity against the target viral protein.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute.
Anne Trafton, MIT News Office
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Phone: 617-253-2700
Fax: 617-258-8762
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








