Home > Press > Just Add Water: How Scientists Are Using Silicon to Produce Hydrogen on Demand - New technology could help power portable devices like satellite phones and radios
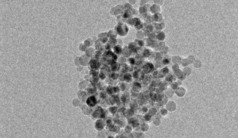 |
| Transmission electron microscopy image showing spherical silicon nanoparticles about 10 nanometers in diameter. These particles, created in a UB lab, react with water to quickly produce hydrogen, according to new UB research. Credit: Swihart Research Group, University at Buffalo. |
Abstract:
Super-small particles of silicon react with water to produce hydrogen almost instantaneously, according to University at Buffalo researchers.
In a series of experiments, the scientists created spherical silicon particles about 10 nanometers in diameter. When combined with water, these particles reacted to form silicic acid (a nontoxic byproduct) and hydrogen — a potential source of energy for fuel cells.
Just Add Water: How Scientists Are Using Silicon to Produce Hydrogen on Demand - New technology could help power portable devices like satellite phones and radios
Buffalo, NY | Posted on January 22nd, 2013The reaction didn't require any light, heat or electricity, and also created hydrogen about 150 times faster than similar reactions using silicon particles 100 nanometers wide, and 1,000 times faster than bulk silicon, according to the study.
The findings appeared online in Nano Letters on Jan. 14. The scientists were able to verify that the hydrogen they made was relatively pure by testing it successfully in a small fuel cell that powered a fan.
"When it comes to splitting water to produce hydrogen, nanosized silicon may be better than more obvious choices that people have studied for a while, such as aluminum," said researcher Mark T. Swihart, UB professor of chemical and biological engineering and director of the university's Strategic Strength in Integrated Nanostructured Systems.
"With further development, this technology could form the basis of a ‘just add water' approach to generating hydrogen on demand," said researcher Paras Prasad, executive director of UB's Institute for Lasers, Photonics and Biophotonics (ILPB) and a SUNY Distinguished Professor in UB's Departments of Chemistry, Physics, Electrical Engineering and Medicine. "The most practical application would be for portable energy sources."
Swihart and Prasad led the study, which was completed by UB scientists, some of whom have affiliations with Nanjing University in China or Korea University in South Korea. Folarin Erogbogbo, a research assistant professor in UB's ILPB and a UB PhD graduate, was first author.
The speed at which the 10-nanometer particles reacted with water surprised the researchers. In under a minute, these particles yielded more hydrogen than the 100-nanometer particles yielded in about 45 minutes. The maximum reaction rate for the 10-nanometer particles was about 150 times as fast.
Swihart said the discrepancy is due to geometry. As they react, the larger particles form nonspherical structures whose surfaces react with water less readily and less uniformly than the surfaces of the smaller, spherical particles, he said.
Though it takes significant energy and resources to produce the super-small silicon balls, the particles could help power portable devices in situations where water is available and portability is more important than low cost. Military operations and camping trips are two examples of such scenarios.
"It was previously unknown that we could generate hydrogen this rapidly from silicon, one of Earth's most abundant elements," Erogbogbo said. "Safe storage of hydrogen has been a difficult problem even though hydrogen is an excellent candidate for alternative energy, and one of the practical applications of our work would be supplying hydrogen for fuel cell power. It could be military vehicles or other portable applications that are near water."
"Perhaps instead of taking a gasoline or diesel generator and fuel tanks or large battery packs with me to the campsite (civilian or military) where water is available, I take a hydrogen fuel cell (much smaller and lighter than the generator) and some plastic cartridges of silicon nanopowder mixed with an activator," Swihart said, envisioning future applications. "Then I can power my satellite radio and telephone, GPS, laptop, lighting, etc. If I time things right, I might even be able to use excess heat generated from the reaction to warm up some water and make tea."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Charlotte Hsu
716-645-4655
Copyright © University at Buffalo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








