Home > Press > Engineers roll up their sleeves ' and then do the same with inductors
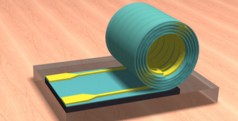 |
| Illinois researchers developed a new design paradigm for inductors. Processed while flat, they then roll up on their own, taking up much less space on a chip. |
Abstract:
On the road to smaller, high-performance electronics, University of Illinois researchers have smoothed one speed bump by shrinking a key, yet notoriously large element of integrated circuits.
Engineers roll up their sleeves ' and then do the same with inductors
Champaign, IL | Posted on December 13th, 2012Three-dimensional rolled-up inductors have a footprint more than 100 times smaller without sacrificing performance. The researchers published their new design paradigm in the journal Nano Letters.
"It's a new concept for old technology," said team leader Xiuling Li, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Illinois.
Inductors, often seen as the sprawling metal spirals on computer chips, are essential components of integrated circuits. They store magnetic energy, acting as a buffer against changes in current and modulating frequency - especially important in radio-frequency wireless devices. However, they take up a lot of space. Inductance depends on the number of coils in the spiral, so engineers cannot make them smaller without losing performance.
In addition, the larger the area the inductor occupies, the more it interfaces with the substrate the chip is built on, exacerbating a hindering effect called parasitic capacitance. Researchers have developed some three-dimensional inductor structures to solve the dual problems of space and parasitic capacitance, but these methods are complex and use techniques that are difficult to scale up to manufacturing levels.
The new inductor design uses techniques Li's group previously developed for making thin films of silicon nitride, merely tens of nanometers in thickness, that roll themselves up into tubes. The research team used industry-standard two-dimensional processing to pattern metal lines on the film before rolling, creating a spiral inductor.
"We're making 3-D structures with 2-D processing," Li said. "Instead of spreading this out in a large area to increase inductance, we can have the same inductance but packed into a much smaller area."
Using the self-rolling technique, the researchers can shrink the area needed for a radio-frequency inductor to a scant 45 microns by 16 microns - more than 100 times smaller than the area an equivalent flat spiral would require.
The design can be adjusted to fit target parameters including metal thickness and type, frequency, tube diameter and number of turns. According to Li, this technique could be used for capacitors and other integrated circuit elements as well.
Now, Li's group is working to produce high-performance inductor prototypes, in collaboration with electrical and engineering professor Jose Schutt-Aine. Preliminary experimental data show strong correlation with the modeled designs.
"Once we have optimized this process, we should be able to make an integrated circuit with a completely different platform that could be much smaller," Li said. "It's an ambitious goal."
The National Science Foundation and the Office of Naval Research supported this work. U. of I. visiting researcher Wen Huang, postdoctoral researcher Xin Yu, graduate student Paul Froeter and mechanical science and engineering professor Placid Ferreira were co-authors of this study. Li also is affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, the Micro and Nanotechnology Lab, and the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Lab, all at the U. of I.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liz Ahlberg
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1073
Xiuling Li
217-265-6354
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hardware
![]() The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
The present and future of computing get a boost from new research July 21st, 2023
![]() A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
A Carbon Nanotube Microprocessor Mature Enough to Say Hello: Three new breakthroughs make commercial nanotube processors possible March 2nd, 2020
![]() Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Powering the future: Smallest all-digital circuit opens doors to 5 nm next-gen semiconductor February 11th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








