Home > Press > Penn Researchers Make Flexible, Low-voltage Circuits Using Nanocrystals
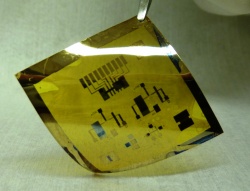 |
| Flexible circuit fabricated in the Kagan lab. (Photo: David Kim and Yuming Lai) |
Abstract:
Electronic circuits are typically integrated in rigid silicon wafers, but flexibility opens up a wide range of applications. In a world where electronics are becoming more pervasive, flexibility is a highly desirable trait, but finding materials with the right mix of performance and manufacturing cost remains a challenge.
Penn Researchers Make Flexible, Low-voltage Circuits Using Nanocrystals
Philadelphia, PA | Posted on November 27th, 2012Now a team of researchers from the University of Pennsylvania has shown that nanoscale particles, or nanocrystals, of the semiconductor cadmium selenide can be "printed" or "coated" on flexible plastics to form high-performance electronics.
The research was led by David Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in Penn's School of Engineering and Applied Science; Yuming Lai, a doctoral student in the Engineering School's Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering; and professor Cherie Kagan, who has appointments in both departments as well as in the School of Arts and Sciences' Department of Chemistry. Benjamin Diroll, a doctoral student in chemistry, and Penn Integrates Knowledge Professor Christopher Murray of Materials Science and of Chemistry also collaborated on the research.
Their work was published in the journal Nature Communications.
"We have a performance benchmark in amorphous silicon, which is the material that runs the display in your laptop, among other devices," Kagan said. "Here, we show that these cadmium selenide nanocrystal devices can move electrons 22 times faster than in amorphous silicon."
Besides speed, another advantage cadmium selenide nanocrystals have over amorphous silicon is the temperature at which they are deposited. Whereas amorphous silicon uses a process that operates at several hundred degrees, cadmium selenide nanocrystals can be deposited at room temperature and annealed at mild temperatures, opening up the possibility of using more flexible plastic foundations.
Another innovation that allowed the researchers to use flexible plastic was their choice of ligands, the chemical chains that extend from the nanocrystals' surfaces and helps facilitate conductivity as they are packed together into a film.
"There have been a lot of electron transport studies on cadmium selenide, but until recently we haven't been able to get good performance out of them," Kim said. "The new aspect of our research was that we used ligands that we can translate very easily onto the flexible plastic; other ligands are so caustic that the plastic actually melts."
Because the nanocrystals are dispersed in an ink-like liquid, multiple types of deposition techniques can be used to make circuits. In their study, the researchers used spincoating, where centrifugal force pulls a thin layer of the solution over a surface, but the nanocrystals could be applied through dipping, spraying or ink-jet printing as well.
On a flexible plastic sheet a bottom layer of electrodes was patterned using a shadow mask — essentially a stencil — to mark off one level of the circuit. The researchers then used the stencil to define small regions of conducting gold to make the electrical connections to upper levels that would form the circuit. An insulating aluminum oxide layer was introduced and a 30-nanometer layer of nanocrystals was coated from solution. Finally, electrodes on the top level were deposited through shadow masks to ultimately form the circuits.
"The more complex circuits are like buildings with multiple floors," Kagan said. "The gold acts like staircases that the electrons can use to travel between those floors."
Using this process, the researchers built three kinds of circuits to test the nanocrystals performance for circuit applications: an inverter, an amplifier and a ring oscillator.
"An inverter is the fundamental building block for more complex circuits," Lai said. "We can also show amplifiers, which amplify the signal amplitude in analog circuits, and ring oscillators, where ‘on' and ‘off' signals are properly propagating over multiple stages in digital circuits."
"And all of these circuits operate with a couple of volts," Kagan said. "If you want electronics for portable devices that are going to work with batteries, they have to operate at low voltage or they won't be useful."
With the combination of flexibility, relatively simple fabrication processes and low power requirements, these cadmium selenide nanocrystal circuits could pave the way for new kinds of devices and pervasive sensors, which could have biomedical or security applications.
"This research also opens up the possibility of using other kinds of nanocrystals, as we've shown the materials aspect is not a limitation any more," Kim said.
The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Evan Lerner
215-573-6604
Copyright © University of Pennsylvania
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








