Home > Press > Research Reveals Nanotechnology Simplifies Hydrogen Production for Clean Energy
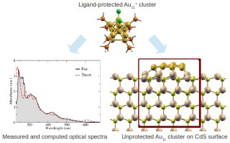 |
| Experimental and theory predicted optical properties of supported sub-nanometer particles. |
Abstract:
In the first-ever experiment of its kind, researchers have demonstrated that clean energy hydrogen can be produced from water splitting by using very small metal particles that are exposed to sunlight. In the article, "Outstanding activity of sub-nm Au clusters for photocatalytic hydrogen production," published in the journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Alexander Orlov, PhD, an Assistant Professor of Materials Science & Engineering at Stony Brook University, and his colleagues from Stony Brook and Brookhaven National Laboratory, found that the use of gold particles smaller than one nanometer resulted in greater hydrogen production than other co-catalysts tested.
Research Reveals Nanotechnology Simplifies Hydrogen Production for Clean Energy
Stony Brook, NY | Posted on November 21st, 2012"This is the first ever demonstration of the remarkable potential of very small metal nanoparticles [containing fewer than a dozen atoms] for making fuel from water," said Professor Orlov. Using nanotechnology, Professor Orlov's group found that when the size of metal particles are reduced to dimensions below one nanometer, there is a tremendous increase in the ability of these particles to facilitate hydrogen production from water using solar light. They observed a "greater than 35 times increase" in hydrogen evolution as compared to ordinary materials.
In order to explain these fascinating results, Professor Orlov collaborated with Brookhaven National Lab computational scientist Dr. Yan Li, who found some interesting anomalies in electronic properties of these small particles. Professor Orlov noted that there is still a tremendous amount of work that needs be done to understand this phenomenon. "It is conceivable that we are only at the beginning of an extraordinary journey to utilize such small particles [of less than a dozen atoms in size] for clean energy production," he said.
"In order to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels it is vital to explore various sustainable energy options," Professor Orlov said. "One possible strategy is to develop a hydrogen-based energy economy, which can potentially offer numerous environmental and energy efficiency benefits. Hydrogen can conceivably be a promising energy source in the future as it is a very clean fuel, which produces water as a final combustion product. The current challenge is to find new materials, which can help to produce hydrogen from sustainable sources, such as water."
Professor Orlov also serves as a faculty member of the Consortium for Inter-Disciplinary Environmental Research at Stony Brook University. Members of his research team include Peichuan Shen and Shen Zhao from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Stony Brook and Dr. Dong Su of the Center for Functional Nanomaterials at Brookhaven National Laboratory.
Editors' Note: This project was partially funded by an $80,588 exploratory grant from the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Stony Brook University
Office of Media Relations
631.632.6310
Copyright © Newswise
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








