Home > Press > Materials scientists make additive-free battery electrodes with nanoparticles
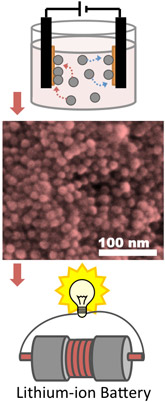 |
| Provided/Richard Robinson Nanoparticle battery electrodes deposited through electrophoretic deposition could lead to lighter and more efficient batteries. At top is a schematic of the EPD process. The middle is an electron microscope image of the nanoparticle electrode. |
Abstract:
Materials scientists have developed a simple, robust way to fabricate carbon-free and polymer-free, lightweight colloidal films for lithium-ion battery electrodes, which could greatly improve battery performance.
Materials scientists make additive-free battery electrodes with nanoparticles
Ithaca, NY | Posted on November 1st, 2012By Anne Ju
By developing a method for additive-free electrodes that maintain high conductivity, the researchers have opened new possibilities for reducing the weight and volume of batteries, while also creating a template system for studying the physics of nanoparticle electrodes.
The work, led by Richard Robinson, assistant professor of materials science and engineering, and graduate student Don-Hyung Ha, is featured in the Oct. 10 issue of Nano Letters (Vol. 12, No. 10).
Nanoparticles have been extensively investigated as an active cathode and anode in lithium-ion batteries -- common components of electronic devices -- because they can enhance the batteries' electrochemical properties.
To use colloidal nanoparticles for the electrodes, it had been necessary to combine them with carbon-based conductive materials for enhancing charge transport, as well as polymeric binders to stick the particles together and to the electrode substrate, Robinson said. This process added extra weight to the battery and made it difficult to model the movement of Li-ions and electrons through the mixture.
The critical processing technique Robinson and colleagues used was electrophoretic deposition, which binds the metal nanoparticles to the surface of the electrode substrate to each other in an assembly, creating strong electrical contacts between the particles and current collector.
The process results in a significant improvement in battery electrode assembly that cannot be replicated by conventional methods. Once attached, the particles are no longer soluble and are mechanically robust. In fact, this processing creates a film that has superior mechanical stability when compared to films fabricated by conventional battery-making methods with binders, Robinson said.
This research has led to the first cobalt-oxide nanoparticle-film battery electrode made without using binders and carbon black additives, and they show high gravimetric and volumetric capacities, even after 50 cycles.
The work was supported by the Energy Materials Center at Cornell funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Science; the Cornell Center for Materials Research with funding from the National Science Foundation; and by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology center at Cornell.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
John Carberry
(607) 255-5553
Cornell Chronicle:
Anne Ju
(607) 255-9735
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








