Home > Press > Solar cell consisting of a single molecule
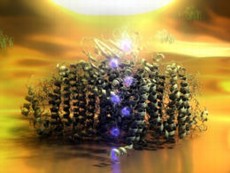 |
| Photosystem-I (green) is optically excited by an electrode (on top). An electron then is transferred step by step in only 16 nanoseconds. Image: Christoph Hohmann (NIM) |
Abstract:
An team of scientists, led by Joachim Reichert, Johannes Barth, and Alexander Holleitner (Technische Universitaet Muenchen, Clusters of Excellence MAP and NIM), and Itai Carmeli (Tel Aviv University) developed a method to measure photocurrents of a single functionalized photosynthetic protein system. The scientists could demonstrate that such a system can be integrated and selectively addressed in artificial photovoltaic device architectures while retaining their biomolecular functional properties. The proteins represent light-driven, highly efficient single-molecule electron pumps that can act as current generators in nanoscale electric circuits. The interdisciplinary team publishes the results in ´Nature Nanotechnology´ this week.
Solar cell consisting of a single molecule
Munich, Germany | Posted on October 2nd, 2012The scientist investigated the photosystem-I reaction center which is a chlorophyll protein complex located in membranes of chloroplasts from cyanobacteria. Plants, algae and bacteria use photosynthesis to convert solar energy into chemical energy. The initial stages of this process - where light is absorbed and energy and electrons are transferred - are mediated by photosynthetic proteins composed of chlorophyll and carotenoid complexes. Until now, none of the available methods were sensitive enough to measure photocurrents generated by a single protein. Photosystem-I exhibits outstanding optoelectronic properties found only in photosynthetic systems. The nanoscale dimension further makes the photosystem-I a promising unit for applications in molecular optoelectronics.
The first challenge the physicists had to master was the development of a method to electrically contact single molecules in strong optical fields. The central element of the realized nanodevice are photosynthetic proteins self-assembled and covalently bound to a gold electrode via cysteine mutation groups. The photocurrent was measured by means of a gold-covered glass tip employed in a scanning near-field optical microscopy set-up. The photosynthetic proteins are optically excited by a photon flux guided through the tetrahedral tip that at the same time provides the electrical contact. With this technique, the physicists were able to monitor the photocurrent generated in single protein units.
The research was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) via the SPP 1243 (grants HO 3324/2 and RE 2592/2), the Clusters of Excellence Munich-Centre for Advanced Photonics and Nanosystems Initiative Munich, as well as ERC Advanced Grant MolArt (no. 47299).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Andreas Battenberg
49-892-891-0510
Dr. Joachim Reichert,
Technische Universitaet Muenchen
Physik-Department E20
James-Franck Strasse, D-85748 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 12443 – Fax:+49 89 289 12338
Prof. Alexander W. Holleitner
Technische Universitaet Muenchen
Walter Schottky Institut – Zentrum für Nanotechnologie und Nanomaterialien
Am Coulombwall 4a, 85748 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 11575 – Fax: +49 89 289 12600
Dr. Itai Carmeli
Tel Aviv University
Center for NanoScience and Nanotechnology and School of Chemistry,
Tel Aviv 69978, Israel.
Tel.: +972-3-6405704 – Fax: +972-3-6405612
Copyright © Technische Universitaet Muenchen
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








