Home > Press > NIST focuses on testing standards to support lab on a chip commercialization
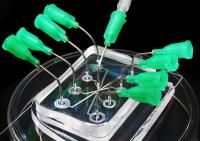 |
| This is a microfluidic lab on a chip device sitting on a polystyrene dish. Stainless steel needles inserted into the apparatus serve as access points for fluids into small channels within it.
Credit: Gregory A. Cooksey/NIST |
Abstract:
Lab on a chip (LOC) devices—microchip-size systems that can prepare and analyze tiny fluid samples with volumes ranging from a few microliters (millionth of a liter) to sub-nanoliters (less than a billionth of a liter)—are envisioned to one day revolutionize how laboratory tasks such as diagnosing diseases and investigating forensic evidence are performed. However, a recent paper* from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) argues that before LOC technology can be fully commercialized, testing standards need to be developed and implemented.
NIST focuses on testing standards to support lab on a chip commercialization
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on August 9th, 2012"A testing standard," explains NIST physical scientist and paper author Samuel Stavis, "defines the procedures used to determine if a lab on a chip device, and the materials from which it is made, conform to specifications." Standardized testing and measurement methods, Stavis writes, will enable MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) LOC manufacturers at all stages of production—from processing of raw materials to final rollout of products—to accurately determine important physical characteristics of LOC devices such as dimensions, electrical surface properties, and fluid flow rates and temperatures.
To make his case for testing standards, Stavis focuses on autofluorescence, the background fluorescent glow of an LOC device that can interfere with the analysis of a sample. Stavis states that multiple factors must be considered in the development of a testing standard for autofluorescence, including: the materials used in the device, the measurement methods used to test the device and how the measurements are interpreted. "All of these factors must be rigorously controlled for, or appropriately excluded from, a meaningful measurement of autofluorescence," Stavis writes.
Quality control during LOC device manufacturing, Stavis says, may require different tests of autofluorescence throughout the process. "There may be one measure of autofluorescence from the block of plastic that is the base material for a chip, another once the block has been fashioned into the substrate in which the functional components are embedded, and yet another as the final device is completed," Stavis says. "To manufacture lab on a chip devices with reliably low autofluorescence, accurate measurements may be needed at each stage."
Stavis also emphasizes that it is important not to confuse testing standards with product standards, and to understand how the former facilitates the latter. "A product standard specifies the technical requirements for a lab on a chip device to be rated as top quality," he says. "A testing standard is needed to measure those specifications, as well as to make fair comparisons between competing products."
* Stavis, S.M. A glowing future for lab on a chip testing standards. Lab on a Chip (2012), DOI: 10.1039/c2lc40511c
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael E. Newman
301-975-3025
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Lab-on-a-chip
![]() Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
Micro-scale opto-thermo-mechanical actuation in the dry adhesive regime Peer-Reviewed Publication September 24th, 2021
![]() Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Silicon-graphene hybrid plasmonic waveguide photodetectors beyond 1.55 μm March 13th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








