Home > Press > Oh, my stars and hexagons! DNA code shapes gold nanoparticles
 |
| Graphic by
Li Huey Tan, Zidong Wang and Yi Lu
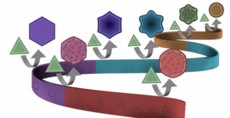
University of Illinois chemists found that DNA can shape gold nanoparticle growth similarly to the way it shapes protein synthesis, with different letters of the genetic code producing gold circles, stars and hexagons. |
Abstract:
DNA holds the genetic code for all sorts of biological molecules and traits. But University of Illinois researchers have found that DNA's code can similarly shape metallic structures.
Oh, my stars and hexagons! DNA code shapes gold nanoparticles
Champaign, IL | Posted on August 8th, 2012The team found that DNA segments can direct the shape of gold
nanoparticles - tiny gold crystals that have many applications in medicine, electronics and catalysis. Led by Yi Lu, the Schenck Professor of Chemistry at the U. of I., the team published its surprising findings in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
"DNA-encoded nanoparticle synthesis can provide us a facile but novel way to produce nanoparticles with predictable shape and properties," Lu said. "Such a discovery has potential impacts in bio-nanotechnology and applications in our everyday lives such as catalysis, sensing, imaging and medicine."
Gold nanoparticles have wide applications in both biology and materials science thanks to their unique physicochemical properties. Properties of a gold nanoparticle are largely determined by its shape and size, so it is critical to be able to tailor the properties of a nanoparticle for a specific application.
"We wondered whether different combinations of DNA sequences could constitute ‘genetic codes' to direct the nanomaterial synthesis in a way similar to their direction of protein synthesis," said Zidong Wang, a recent graduate of Lu's group and the first author of the paper.
Gold nanoparticles are made by sewing tiny gold seeds in a solution of gold salt. Particles grow as gold in the salt solution deposits onto the seeds. Lu's group incubated the gold seeds with short segments of DNA before adding the salt solution, causing the particles to grow into various shapes determined by the genetic code of the DNA.
The DNA alphabet comprises four letters: A, T, G and C. The term genetic code refers to the sequence of these letters, called bases. The four bases and their combinations can bind differently with facets of gold nanoseeds and direct the nanoseeds' growth pathways, resulting in different shapes.
In their experiments, the researchers found that strands of repeating A's produced rough, round gold particles; T's, stars; C's, round, flat discs; G's, hexagons. Then the group tested DNA strands that were a combination of two bases, for example, 10 T's and 20 A's. They found that many of the bases compete with each other resulting in intermediate shapes, although A dominates over T.
Next, the researchers plan to investigate exactly how DNA codes direct nanoparticle growth. They also plan to apply their method to synthesize other types of nanomaterials with novel applications.
The National Science Foundation supported this work.
Lu also is affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology and with the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory, both of which are at the U. of I.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liz Ahlberg
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1073
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








