Home > Press > New fuel cell keeps going after the hydrogen runs out: Materials scientists demonstrate first SOFC capable of battery-like storage
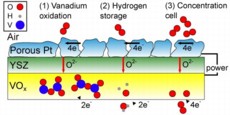 |
| Three possible mechanisms (left to right) can explain the operation of the vanadium oxide / platinum fuel cell after its fuel has been spent. The illustration represents a simplified cross-section of the SOFC: the top layer is the cathode (made of porous platinum), the middle layer is the electrolyte (yttria-stabilized zirconia, YSZ), and the bottom layer is the VOx anode. During normal operation, the hydrogen fuel would be at the bottom of this diagram. (Image courtesy of Quentin Van Overmeere.) |
Abstract:
Imagine a kerosene lamp that continued to shine after the fuel was spent, or an electric stove that could remain hot during a power outage.
Materials scientists at Harvard have demonstrated an equivalent feat in clean energy generation with a solid-oxide fuel cell (SOFC) that converts hydrogen into electricity but can also store electrochemical energy like a battery. This fuel cell can continue to produce power for a short time after its fuel has run out.
New fuel cell keeps going after the hydrogen runs out: Materials scientists demonstrate first SOFC capable of battery-like storage
Cambridge, MA | Posted on June 30th, 2012"This thin-film SOFC takes advantage of recent advances in low-temperature operation to incorporate a new and more versatile material," explains principal investigator Shriram Ramanathan, Associate Professor of Materials Science at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS). "Vanadium oxide (VOx) at the anode behaves as a multifunctional material, allowing the fuel cell to both generate and store energy."
The finding, which appears online in the journal Nano Letters, will be most important for small-scale, portable energy applications, where a very compact and lightweight power supply is essential and the fuel supply may be interrupted.
"Unmanned aerial vehicles, for instance, would really benefit from this," says lead author Quentin Van Overmeere, a postdoctoral fellow at SEAS. "When it's impossible to refuel in the field, an extra boost of stored energy could extend the device's lifespan significantly."
Ramanathan, Van Overmeere, and their coauthor Kian Kerman (a graduate student at SEAS) typically work on thin-film SOFCs that use platinum for the electrodes (the two "poles" known as the anode and the cathode). But when a platinum-anode SOFC runs out of fuel, it can continue to generate power for only about 15 seconds before the electrochemical reaction peters out.
The new SOFC uses a bilayer of platinum and VOx for the anode, which allows the cell to continue operating without fuel for up to 14 times as long (3 minutes, 30 seconds, at a current density of 0.2 mA/cm2). This early result is only a "proof of concept," according to Ramanathan, and his team predicts that future improvements to the composition of the VOx-platinum anode will further extend the cell's lifespan.
During normal operation, the amount of power produced by the new device is comparable to that produced by a platinum-anode SOFC. Meanwhile, the special nanostructured VOx layer sets up various chemical reactions that continue after the hydrogen fuel has run out.
"There are three reactions that potentially take place within the cell due to this vanadium oxide anode," says Ramanathan. "The first is the oxidation of vanadium ions, which we verified through XPS (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy). The second is the storage of hydrogen within the VOx crystal lattice, which is gradually released and oxidized at the anode. And the third phenomenon we might see is that the concentration of oxygen ions differs from the anode to the cathode, so we may also have oxygen anions being oxidized, as in a concentration cell."
All three of those reactions are capable of feeding electrons into a circuit, but it is currently unclear exactly what allows the new fuel cell to keep running. Ramanathan's team has so far determined experimentally and quantitatively that at least two of three possible mechanisms are simultaneously at work.
Ramanathan and his colleagues estimate that a more advanced fuel cell of this type, capable of producing power without fuel for a longer period of time, will be available for applications testing (e.g., in micro-air vehicles) within 2 years.
This work was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), a postdoctoral scholarship from Le Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique-FNRS, and the U.S. Department of Defense's National Defense Science and Engineering Graduate Fellowship Program. The researchers also benefited from the resources of the Harvard University Center for Nanoscale Systems (a member of the NSF-funded National Nanotechnology Infrastructure Network) and the NSF-funded MRSEC Shared Experimental Facilities at MIT.
####
Contacts:
Caroline Perry
(617) 496-1351
Copyright © Harvard's School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Fuel Cells
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








