Home > Press > Rice researchers develop paintable battery: Technique could turn any surface into a lithium-ion battery; may be combined with solar cells
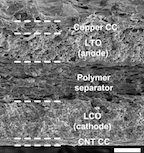 |
| An electron microscope image of a spray-painted lithium-ion battery developed at Rice University shows its five-layer structure. (Credit: Ajayan Lab/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Researchers at Rice University have developed a lithium-ion battery that can be painted on virtually any surface.
Rice researchers develop paintable battery: Technique could turn any surface into a lithium-ion battery; may be combined with solar cells
Houston, TX | Posted on June 29th, 2012The rechargeable battery created in the lab of Rice materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan consists of spray-painted layers, each representing the components in a traditional battery. The research appears today in Nature's online, open-access journal Scientific Reports.
"This means traditional packaging for batteries has given way to a much more flexible approach that allows all kinds of new design and integration possibilities for storage devices," said Ajayan, Rice's Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science and of chemistry. "There has been lot of interest in recent times in creating power sources with an improved form factor, and this is a big step forward in that direction."
Lead author Neelam Singh, a Rice graduate student, and her team spent painstaking hours formulating, mixing and testing paints for each of the five layered components - two current collectors, a cathode, an anode and a polymer separator in the middle.
The materials were airbrushed onto ceramic bathroom tiles, flexible polymers, glass, stainless steel and even a beer stein to see how well they would bond with each substrate.
In the first experiment, nine bathroom tile-based batteries were connected in parallel. One was topped with a solar cell that converted power from a white laboratory light. When fully charged by both the solar panel and house current, the batteries alone powered a set of light-emitting diodes that spelled out "RICE" for six hours; the batteries provided a steady 2.4 volts.
The researchers reported that the hand-painted batteries were remarkably consistent in their capacities, within plus or minus 10 percent of the target. They were also put through 60 charge-discharge cycles with only a very small drop in capacity, Singh said.
Each layer is an optimized stew. The first, the positive current collector, is a mixture of purified single-wall carbon nanotubes with carbon black particles dispersed in N-methylpyrrolidone. The second is the cathode, which contains lithium cobalt oxide, carbon and ultrafine graphite (UFG) powder in a binder solution. The third is the polymer separator paint of Kynar Flex resin, PMMA and silicon dioxide dispersed in a solvent mixture. The fourth, the anode, is a mixture of lithium titanium oxide and UFG in a binder, and the final layer is the negative current collector, a commercially available conductive copper paint, diluted with ethanol.
"The hardest part was achieving mechanical stability, and the separator played a critical role," Singh said. "We found that the nanotube and the cathode layers were sticking very well, but if the separator was not mechanically stable, they would peel off the substrate. Adding PMMA gave the right adhesion to the separator." Once painted, the tiles and other items were infused with the electrolyte and then heat-sealed and charged.
Singh said the batteries were easily charged with a small solar cell. She foresees the possibility of integrating paintable batteries with recently reported paintable solar cells to create an energy-harvesting combination that would be hard to beat. As good as the hand-painted batteries are, she said, scaling up with modern methods will improve them by leaps and bounds. "Spray painting is already an industrial process, so it would be very easy to incorporate this into industry," Singh said.
The Rice researchers have filed for a patent on the technique, which they will continue to refine. Singh said they are actively looking for electrolytes that would make it easier to create painted batteries in the open air, and they also envision their batteries as snap-together tiles that can be configured in any number of ways.
"We really do consider this a paradigm changer," she said.
Co-authors of the paper are graduate students Charudatta Galande and Akshay Mathkar, alumna Wei Gao, now a postdoctoral researcher at Los Alamos National Laboratory, and research scientist Arava Leela Mohana Reddy, all of Rice; Rice Quantum Institute intern Andrea Miranda; and Alexandru Vlad, a former research associate at Rice, now a postdoctoral researcher at the Université Catholique de Louvain, Belgium.
The Advanced Energy Consortium, the National Science Foundation Partnerships for International Research and Education, Army Research Laboratories and Nanoholdings Inc. supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is known for its “unconventional wisdom.” With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 4 for “best value” among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to www.rice.edu/nationalmedia/Rice.pdf.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








