Home > Press > Study Improves Understanding of Surface Molecules in Controlling Size of Gold Nanoparticles
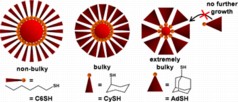 |
| The bulkier the ligand, the fewer ligands can sit side-by-side -- leading to a smaller nanoparticle. |
Abstract:
Use of bulky ligands (BLs) in the synthesis of metal nanoparticles (NPs) gives smaller core sizes, sharpens the size distribution, and alters the discrete sizes. For BLs, the highly curved surface of small NPs may facilitate growth, but as the size increases and the surface flattens, NP growth may terminate when the ligand monolayer blocks BLs from transporting metal atoms to the NP core. Batches of thiolate-stabilized Au NPs were synthesized using equimolar amounts of 1-adamantanethiol (AdSH), cyclohexanethiol (CySH), or n-hexanethiol (C6SH). The bulky CyS- and AdS-stabilized NPs have smaller, more monodisperse sizes than the C6S-stabilized NPs. As the bulkiness increases, the near-infrared luminescence intensity increases, which is characteristic of small Au NPs. Four new discrete sizes were measured by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, Au30(SAd)18, Au39(SAd)23, Au65(SCy)30, and Au67(SCy)30. No Au25(SAd)18 was observed, which suggests that this structure would be too sterically crowded. Use of BLs may also lead to the discovery of new discrete sizes in other systems.
Study Improves Understanding of Surface Molecules in Controlling Size of Gold Nanoparticles
Raleigh, NC | Posted on June 18th, 2012North Carolina State University researchers have shown that the "bulkiness" of molecules commonly used in the creation of gold nanoparticles actually dictates the size of the nanoparticles - with larger so-called ligands resulting in smaller nanoparticles. The research team also found that each type of ligand produces nanoparticles in a particular array of discrete sizes.
"This work advances our understanding of nanoparticle formation, and gives us a new tool for controlling the size and characteristics of gold nanoparticles," says Dr. Joseph Tracy, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper describing the research. Gold nanoparticles are used in industrial chemical processes, as well as medical and electronics applications.
When creating gold nanoparticles, scientists often use organic molecules called ligands to facilitate the process. The ligands effectively bring gold atoms together in a solution to create the nanoparticles. In the process, ligands essentially line up side by side and surround the nanoparticles in all three dimensions.
The researchers wanted to see whether the bulkiness of the ligands affected nanoparticle size, and opted to assess three types of thiol ligands - a family of ligands commonly used to synthesize gold nanoparticles. Specifically, the molecules bound to the gold nanoparticles are linear hexanethiolate (-SC6), cyclohexanethiolate (-SCy) and 1-adamantanethiolate (-SAd). Each of these ligands has a bulkier configuration than the last.
For example, picture each ligand as a slice of pie, with a gold atom attached to the pointed end. -SC6 looks like a very narrow slice of pie. -SCy is slightly larger, and -SAd is the largest of the three - with the "crust" end of the pie wedge far wider than the pointed end.
The researchers found that the bulkiness of the ligands determined the size of the nanoparticles. Because fewer -SAd and -SCy ligands can line up next to each other in three dimensions, fewer gold atoms are brought together in the core. Therefore, the nanoparticles are smaller. -SC6, the least bulky of the thiolates, can create the largest nanoparticles.
"While we've shown that this is an effective means of controlling size in gold nanoparticles, we think it may have implications for other materials as well," says Peter Krommenhoek, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of the paper. "That's something we're exploring."
But the researchers made another interesting finding as well.
When particularly small nanoparticles form, they tend to form at very specific sizes, called discrete sizes. For instance, some types of nanoparticles may consist of 25 or 28 atoms - but never 26 or 27 atoms.
In this study, the researchers found that the bulkiness of the ligands also changed the discrete sizes of the nanoparticles. "This is interesting, in part, because each discrete size represents a different number of gold atoms and ligands," Tracy says, "which could influence the nanoparticle's chemical behavior. That question has yet to be addressed."
The paper, "Bulky Adamantanethiolate and Cyclohexanethiolate Ligands Favor Smaller Gold Nanoparticles with Altered Discrete Sizes," was published online June 15 in ACS Nano. The paper was co-authored by Dr. Junwei Wang, a former postdoctoral research associate at NC State; Dr. Nathaniel Hentz, of the Golden LEAF Biomanufacturing Training and Education Center at NC State; Krystian Kozek, a former undergraduate at NC State; Dr. Aaron Johnston-Peck, a postdoctoral researcher at Brookhaven National Laboratory; and Dr. Gregory Kalyuzhny of San Diego State University.
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Education.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
News Services
919.515.6386
Dr. Joe Tracy
919.513.2623
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








