Home > Press > The finest gold dust in the world
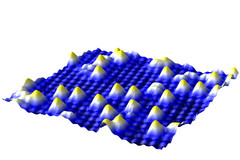 |
| SMT-Image of the iron-oxide surface - with gold atoms on top Copyright: Vienna University of Technology |
Abstract:
Scientists at the Vienna University of Technology found a method to locate single gold atoms on a surface. This should pave the way to better and cheaper catalysts.
The finest gold dust in the world
Vienna, Austria | Posted on May 30th, 2012Most people value large chunks of gold - but scientists at the Vienna University of Technology are interested in gold at the smallest possible scale, because single gold atoms are potentially the most reactive catalysts for chemical reactions. However, when gold atoms are placed on a surface they tend to ball up into tiny nuggets consisting of several atoms. A team of surface scientists now managed to fix single gold atoms on special sites of an iron-oxide surface. This could open the door to more efficient catalysts, requiring less of the precious material.
Gold Does Not Like to Be Alone
Gold is a noble metal and does not usually bond with other elements, but as a catalyst it facilitates chemical reactions. It can, for example, facilitate the conversion of poisonous carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide. The effectiveness of gold as a catalyst depends on the size of the gold particles. Some evidence suggests that it works best if the gold is present in the form of single atoms. So far, however, this could not be studied in detail. "If individual gold atoms are put on a surface, they usually cluster up, forming nanoparticles", says Gareth Parkinson, who oversaw the experiments in the research group of Professor Ulrike Diebold at the Institute for Applied Physics at the TU Vienna.
Hot Surfaces - Loose Atoms
Higher temperatures lead to a higher mobility of the gold atoms, so in order to stop the atoms from clustering, most surfaces must be cooled to a temperature so low that the desired chemical reactions would stop entirely. The researchers at the TU Vienna found a special kind of iron-oxide surface, which locks the single gold atoms in place.
A Good Place to Settle Down
The key to success is a slight deformation of the iron-oxide crystal structure. The oxygen atoms of the topmost layer are not aligned in perfectly straight lines, they are bent into wiggles by the atoms below. At the points where the lines of oxygen atoms are close to each other, the gold atoms attach permanently without losing grip. Even if the surface is heated, the gold atoms stay put - only at 500 degrees celsius they start forming clusters.
"When a gold atom hits the iron oxide surface, it diffuses to one of the sites where it can be attached to the surface", says Gareth Parkinson. That way, many single gold atoms can be placed close to each other. When a gold atom hits a position already occupied by another gold atom, however, the two bond and start moving across the surface, picking up additional gold atoms along the way. When they have reached a critical size of at least five atoms, they become immobile again and the miniature gold nugget comes to rest.
New Paths for New Research
Ulrike Diebold expects that the new method will answer important open questions about catalysis. "We have created an ideal model system for probing the chemical reactivity of single atomic species", says Diebold. The recent experiments will also help to advance theoretical research: the quantum mechanically complex bonding between single atoms and this particular surfaces provide an excellent test case for theoretical calculations of highly correlated electron systems.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Florian Aigner
43-158-801-41027
Prof. Ulrike Diebold
Institute for Applied Physics
Vienna University of Technology
Wiedner Hauptstraße 8, 1040 Vienna
T: +43-1-58801-13425
Gareth Parkinson, PhD
Institute for Applied Physics
Vienna University of Technology
Wiedner Hauptstraße 8, 1040 Vienna
T: +43-1-58801-13473
Copyright © Vienna University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








