Home > Press > New ultra-thin electronic films have greater capacity
 |
| Macromolecule containing sub-units (blocks) of several types. Here, an assembly of two types of blocks. |
Abstract:
The development of a new combination of polymers associating sugars with oil-based macromolecules makes it possible to design ultra-thin films capable of self-organization with a 5-nanometer resolution. This opens up new horizons for increasing the capacity of hard discs and the speed of microprocessors. The result of a French-American collaboration spearheaded by the Centre de Recherches sur les Macromolécules Végétales (CNRS), this work has led to the filing of two patents. It is published in the journal ACS Nano. This new class of thin films based on hybrid copolymers could give rise to numerous applications in flexible electronics, in areas as diverse as nanolithography, biosensors and photovoltaic cells.
New ultra-thin electronic films have greater capacity
Paris, France | Posted on May 12th, 2012Before new generations of microprocessors can be devised, an evolution in lithography, the technique used for printing electronic circuits, is indispensable. Until now, the thin films used in electronic circuits have been designed from synthetic polymers exclusively derived from petroleum. However, these thin films have limitations: their minimum structural resolution is around 20 nanometers and cannot be reduced further by combining petroleum-derived polymers. This limit has been one of the main obstacles to the development of new generations of very-high-resolution flexible electronic devices.
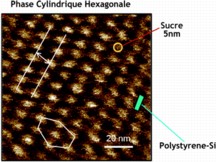
Why was there such a limit? Because of the low incompatibility between the two blocks of polymers, both derived from oil. For that reason, the team headed by Redouane Borsali, CNRS senior researcher at the Centre de Recherches sur les Macromolécules Végétales (CERMAV), came up with a hybrid material: this new class of thin films combines sugar-based and petroleum-derived (silicon containing polystyrene) polymers with widely different physical/chemical characteristics. This copolymer(1), formed of highly incompatible elementary building blocks, is similar to an oil bubble attached to a small water bubble. The researchers have shown that this type of structure is capable of organizing itself into sugar cylinders within a petroleum-based polymer lattice, each structure having a size of 5 nanometers, i.e. much smaller than the resolution of "old" copolymers, exclusively composed of petroleum derivatives. In addition, this new generation of material is made from an abundant, renewable and biodegradable resource: sugar.
Achieving this performance makes it possible to envisage numerous applications in flexible electronics: miniaturization of circuit lithography, six-fold increase in information storage capacity (flash memories - USB keys - no longer limited to 1 Tbit of data but 6 Tbit), enhanced performance of photovoltaic cells, biosensors, etc. The researchers are now seeking to improve control of these nano-glycofilms' large-scale organization and design in different self-organized structures.
These results follow prior work carried out by CERMAV within the framework of the Grenoble RTRA (Thematic Network of Advanced Research) "Nanosciences at the limits of nanolectronics".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Julien Guillaume
+ 33 1 44 96 51 51
CNRS researcher
Redouane Borsali
T +33 (0)4 76 03 76 40 l
CNRS press officer
Priscilla Dacher
T +33 (0)1 44 96 46 06 l
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








