Home > Press > Light touch keeps a grip on delicate nanoparticles
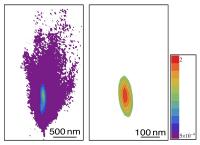 |
| NIST researchers' new approach to trapping nanoparticles uses a control and feedback system that nudges them only when needed, lowering the average intensity of the beam and increasing the lifetime of the nanoparticles while reducing their tendency to wander. On the left, 100-nanometer gold nanoparticles quickly escape from a static trap while gold nanoparticles trapped using the NIST method remained strongly confined.
Credit: NIST |
Abstract:
Using a refined technique for trapping and manipulating nanoparticles, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have extended the trapped particles' useful life more than tenfold.* This new approach, which one researcher likens to "attracting moths," promises to give experimenters the trapping time they need to build nanoscale structures and may open the way to working with nanoparticles inside biological cells without damaging the cells with intense laser light.
Light touch keeps a grip on delicate nanoparticles
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on May 4th, 2012Scientists routinely trap and move nanoparticles in a solution with "optical tweezers"—a laser focused to a very small point. The tiny dot of laser light creates a strong electric field, or potential well, that attracts particles to the center of the beam. Although the particles are attracted into the field, the molecules of the fluid they are suspended in tend to push them out of the well. This effect only gets worse as particle size decreases because the laser's influence over a particle's movement gets weaker as the particle gets smaller. One can always turn up the power of the laser to generate a stronger electric field, but doing that can fry the nanoparticles too quickly to do anything meaningful with them—if it can hold them at all.
NIST researchers' new approach uses a control and feedback system that nudges the nanoparticle only when needed, lowering the average intensity of the beam and increasing the lifetime of the nanoparticle while reducing its tendency to wander. According to Thomas LeBrun, they do this by turning off the laser when the nanoparticle reaches the center and by constantly tracking the particle and moving the tweezers as the particle moves.
"You can think of it like attracting moths in the dark with a flashlight," says LeBrun. "A moth is naturally attracted to the flashlight beam and will follow it even as the moth flutters around apparently at random. We follow the fluttering particle with our flashlight beam as the particle is pushed around by the neighboring molecules in the fluid. We make the light brighter when it gets too far off course, and we turn the light off when it is where we want it to be. This lets us maximize the time that the nanoparticle is under our control while minimizing the time that the beam is on, increasing the particle's lifetime in the trap."
Using this method at constant average beam power, 100-nanometer gold particles remained trapped 26 times longer than had been seen in previous experiments. Silica particles 350 nanometers in diameter lasted 22 times longer, but with the average beam power reduced by 33 percent. LeBrun says that their approach should be able to be combined with other techniques to trap and hold even smaller nanoparticles for extended periods without damaging them.
"We're more than an order of magnitude ahead of where we were before," says LeBrun. "We now hope to begin building complex nanoscale devices and testing nanoparticles as sensors and drugs in living cells."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mark Esser
301-975-8735
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








