Home > Press > Designing Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery
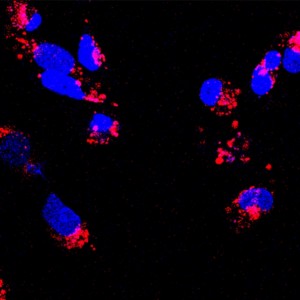 |
| Confocal laser scanning microscopy images of the protein-based nanoparticles incubated with breast cancer cells. |
Abstract:
Natural biological entities have been highly successful in fabricating nanoscale structures and functional systems, leading to scientific exploration of biologically inspired strategies for materials design. In particular, protein-based materials can combine natural properties, structural elements, and biologically reactive sites to obtain self-assembled nanoarchitectures with applications including tissue engineering, nanomaterials synthesis, and drug delivery. However, the functionality of these materials can be limited by the locations or absence of specific chemical conjugation sites.
Designing Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery
Germany | Posted on April 26th, 2012To circumvent this limitation, an investigation by Ren et al., at the University of California, Irvine, implemented a novel, non-covalent strategy to attach guest molecules into a protein-based nanocapsule. Their biomimetic inspiration was multi-drug efflux transporters, which bind a remarkably broad range of structurally-divergent molecules using phenylalanine, a hydrophobic amino acid. Through protein engineering, the team introduced targeted non-native phenylalanines into the hollow cavity of a caged protein scaffold.
The transformed nanoparticles enabled the antitumor drug doxorubicin to bind to the cavity at high loading capacities. These drug-protein complexes could subsequently be applied to induce death in breast cancer cells. Significantly, this work demonstrates a generalized strategy to engineer binding domains within protein-based materials that does not rely on conventional chemical coupling, thus extending the potential functionality of such materials.
Source: University of California, Irvine
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








