Home > Press > Novel prostate nanomedicine delivers high drug concentration directly and safely to tumors in phase I trials : Highly-Targeted Nanoparticles Act as “Trojan Horse” to Deliver Powerful Chemotherapy Agent Without Affecting Healthy Cells
 |
Abstract:
Nanomedicine research at the David H. Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at MIT funded by a $5 million grant from the Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF) has delivered the first nanomedicine shown to successfully target prostate cancer cells and deliver docetaxel chemotherapy in high concentrations in Phase I clinical trials. Docetaxel is used in prostate cancer patients who have failed hormone therapy and is currently delivered via infusion which floods the body and affects both cancerous and healthy cells. By using targeted nanoparticles to deliver the therapeutic, healthy cells are widely spared from undesired side effects of treatment.
Novel prostate nanomedicine delivers high drug concentration directly and safely to tumors in phase I trials : Highly-Targeted Nanoparticles Act as “Trojan Horse” to Deliver Powerful Chemotherapy Agent Without Affecting Healthy Cells
Santa Monica, CA | Posted on April 4th, 2012Results from Phase I clinical trials of BIND-014 were published today in Science Translational Medicine. BIND Biosciences, the biopharmaceutical company that developed BIND-014, also presented the trials data today at the 2012 American Association of Cancer Research meeting in Chicago.
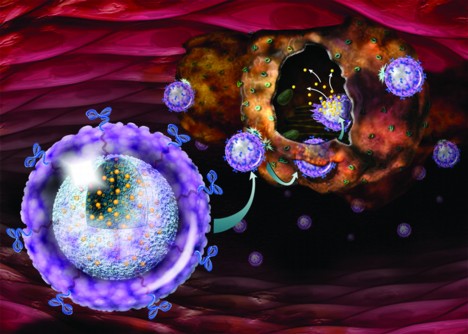
BIND-014 is a programmable nanomedicine that combines a targeting ligand and a therapeutic nanoparticle. BIND-014 contains docetaxel, a proven cancer drug which is approved in major cancer indications including breast, prostate and lung, encapsulated in FDA-approved biocompatible and biodegradable polymers. BIND-014 is targeted to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA), a cell surface antigen abundantly expressed on the surface of cancer cells and on new blood vessels that feed a wide array of solid tumors. In preclinical cancer models, BIND-014 was shown to deliver ten-fold more docetaxel to tumors than an equivalent dose of conventional docetaxel. The increased accumulation of docetaxel at the site of disease translated to marked improvements in antitumor activity and tolerability.
PCF has funded research on PSMA, the attractor antigen or "sticky tape" that is targeted by BIND-014 nanoparticles since 1996. This research further discovered that PSMA is also found on the surfaces of neovasculature (new blood vessels) in the tumors of other cancers.
"The development of BIND-014 represents a unique public, private, and philanthropic funding effort to fast-forward and realize the potential of nanomedicines for the benefit of cancer patients," said Jonathan W. Simons, MD, president and CEO of the Prostate Cancer Foundation which provided $5 million to the collaborative research project in 2007. "This is a tour de force of transdisciplinary collaboration—bioengineers, chemical engineers, nanotechnologists, oncologists, and prostate cancer biologists all came together to advance multiple components and concepts to the clinic. PCF's funding leveraged an early and significant NCI nanotechnology investment in this prostate cancer therapeutics research. With this exemplary new work across institutional boundaries, BIND-014 represents an entirely new, programmable platform for targeted, cancer drug delivery— and it moved to the clinic in a strikingly short period of time."
The idea to develop aptamer-targeted nanoparticles was first conceived in 2002 and forwarded by the David H. Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at MIT, Brigham and Women's Hospital, the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School and Weill Cornell Medical College. Funding for the research and development program was provided by both public and private sources including the MIT Institute for Integrative Center for Cancer Research, the National Institute for Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, a prostate cancer SPORE Grant awarded to Dana Farber Cancer, the National Cancer Institute, the NCI Alliance in Nanotechnology and the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
"These seminal data on BIND's first clinical stage Accurin, BIND-014, demonstrates for the first time that it is possible to generate medicines with both targeted and programmable properties that can concentrate the therapeutic effect directly at the site of disease, potentially revolutionizing how complex diseases such as cancer are treated," commented Omid Farokhzad, M.D, BIND Founder and Associate Professor, Harvard Medical School. "BIND's data are a giant leap forward in achieving the true promise of nanomedicine by enabling the design of therapeutics with highly-differentiated efficacy and safety that go above and beyond the capabilities of traditional drug design through medicinal chemistry."
"Previous attempts to develop targeted nanoparticles have not translated into clinical success because of the inherent difficulty of designing and scaling up a particle capable of targeting, long-circulation via immune-response evasion, and controlled drug release," commented Robert Langer, Sc.D., BIND Founder and David H. Koch Institute Professor at MIT. "BIND-014 is the first therapeutic of its kind to reach clinical evaluation and has demonstrated an increases of up to ten fold in drug concentration in tumors, which lead to substantially better efficacy and safety."
With these findings, multiple Phase I/II trials targeting other cancers expressing PSMA can be accelerated safely.
####
About Prostate Cancer Foundation
The Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF) is the world’s leading philanthropic organization funding and accelerating research. Founded in 1993 by Michael Milken, PCF has raised more than $479 million and provided funding to over 1,600 research projects at nearly 200 institutions in 15 countries around the world. Since 2008, it has supported 98 Young Investigators in seven countries and launched 17 PCF team science Challenge Awards. PCF advocates for greater awareness of prostate cancer and more efficient investment of governmental research funds supporting transformational cancer research. Prostate Cancer Foundation efforts over 19 years have helped produce a 20-fold increase in government funding for prostate cancer and fast-forward research on four new Food and Drug Administration (FDA) drugs for advanced prostate cancer in the past two years.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dan Zenka
Vice President
Communications
Direct: 310.570.4714
Cara Lasala
APR
Sr. Public Relations Specialist
Direct: 310.570.4727
Copyright © Prostate Cancer Foundation
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








