Home > Press > Graphene: Scientists produce graphene using microorganisms
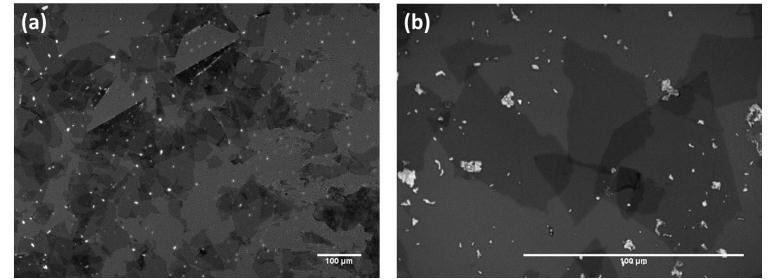 |
| Image of reduced GO sheets on a SiO2/Si substrate. (a) Optical microscope image; and (b) higher magnification. |
Abstract:
The Graphene Research Group at Toyohashi Tech report on the synthesis of graphene by reducing graphene oxide using microorganisms extracted from a local river.
Graphene: Scientists produce graphene using microorganisms
Toyohashi, Japan | Posted on March 22nd, 2012The Toyohashi Tech Graphene Research Group at the Electronics Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS) report on an innovative method for producing high quality graphene by reducing graphene oxide flakes using easily extractable microorganisms.
Currently, the chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO) flakes is the preferred choice for the mass production of graphene. Notably, the critical stage of reducing GO flakes into the 2-dimensional layers of carbon known as graphene involves exposure of the GO to hydrazine. This reduction processes have fundamental limitations for large scale production, in particular because of the hydrazine vapor is highly toxic.
The method developed by the Toyohashi Tech team was inspired by a recent report that graphene oxide behaves as a terminal electron acceptor for bacteria, where the GO is reduced by microbial action in the process of breathing or electron transport. Notably, the Toyohashi Graphene Research Group method is a hybrid approach, where chemically derived graphene oxide flakes are reduced by readily available microorganisms extracted from a river bank near the Tempaku Campus of Toyohashi University of Technology, Aichi, Japan. Raman scattering measurements showed that the GO flakes had indeed been reduced.
####
About Toyohashi University of Technology (Toyohashi Tech)
Founded in 1976, Toyohashi University of Technology is a vibrant modern institute with research activities reflecting the modern era of advanced electronics, engineering, and life sciences.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ms. Junko Sugaya and
Mr. Masashi Yamaguchi
International Affairs Division
TEL: (+81) 0532-44-2042
FAX: (+81)0532-44-6557
Copyright © Toyohashi University of Technology (Toyohashi Tech)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Y. Tanizawa et al 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 352 012011 doi:10.1088/1742-6596/352/1/012011:
Y. Tanizawa et al 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 352 012011 doi:10.1088/1742-6596/352/1/012011:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








