Home > Press > Straintronics: Engineers create piezoelectric graphene
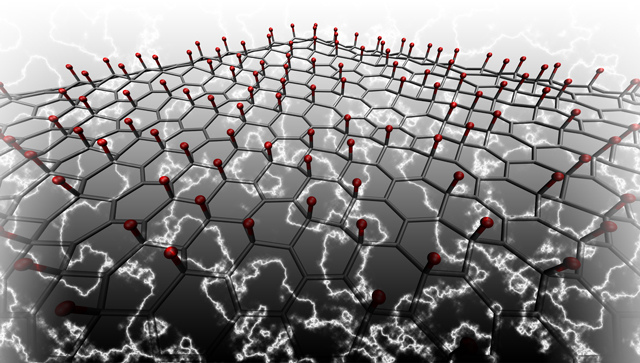 |
| This illustration shows lithium atoms (red) adhered to a graphene lattice that will produce electricity when bent, squeezed or twisted. Conversely, the graphene will deform when an electric field is applied, opening new possibilities in nanotechnology. Illustration: Mitchell Ong, Stanford School of Engineering |
Abstract:
By depositing atoms on one side of a grid of the "miracle material" graphene, researchers at Stanford have engineered piezoelectricity into a nanoscale material for the first time. The implications could yield dramatic degree of control in nanotechnology.
Straintronics: Engineers create piezoelectric graphene
Stanford, CA | Posted on March 21st, 2012By Andrew Myers
In what became known as the ‘Scotch tape technique," researchers first extracted graphene with a piece of adhesive in 2004. Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb, hexagonal pattern. It looks like chicken wire.
Graphene is a wonder material. It is a one-hundred-times-better conductor of electricity than silicon. It is stronger than diamond. And, at just one atom thick, it is so thin as to be essentially a two-dimensional material. Such promising physics have made graphene the most studied substance of the last decade, particularly in nanotechnology. In 2010, the researchers who first isolated it shared the Nobel Prize.
Yet, while graphene is many things, it is not piezoelectric. Piezoelectricity is the property of some materials to produce electric charge when bent, squeezed or twisted. Perhaps more importantly, piezoelectricity is reversible. When an electric field is applied, piezoelectric materials change shape, yielding a remarkable level of engineering control.
Piezoelectrics have found application in countless devices from watches, radios and ultrasound to the push-button starters on propane grills, but these uses all require relatively large, three-dimensional quantities of piezoelectric materials.
Now, in a paper published in the journal ACS Nano, two materials engineers at Stanford have described how they have engineered piezoelectrics into graphene, extending for the first time such fine physical control to the nanoscale.
Straintronics
"The physical deformations we can create are directly proportional to the electrical field applied. This represents a fundamentally new way to control electronics at the nanoscale," said Evan Reed, head of the Materials Computation and Theory Group at Stanford and senior author of the study.
This phenomenon brings new dimension to the concept of ‘straintronics,' he said, because of the way the electrical field strains—or deforms—the lattice of carbon, causing it to change shape in predictable ways.
"Piezoelectric graphene could provide an unparalleled degree of electrical, optical or mechanical control for applications ranging from touchscreens to nanoscale transistors," said Mitchell Ong, a post-doctoral scholar in Reed's lab and first author of the paper.
Using a sophisticated modeling application running on high-performance supercomputers, the engineers simulated the deposition of atoms on one side of a graphene lattice — a process known as doping — and measured the piezoelectric effect.
They modeled graphene doped with lithium, hydrogen, potassium and fluorine, as well as combinations of hydrogen and fluorine and lithium and fluorine on either side of the lattice. Doping just one side of the graphene, or doping both sides with different atoms, is key to the process as it breaks graphene's perfect physical symmetry, which otherwise cancels the piezoelectric effect.
The results surprised both engineers.
"We thought the piezoelectric effect would be present, but relatively small. Yet, we were able to achieve piezoelectric levels comparable to traditional three-dimensional materials," said Reed. "It was pretty significant."
Designer piezoelectricity
The researchers were further able to fine tune the effect by pattern doping the graphene—selectively placing atoms in specific sections and not others.
"We call it designer piezoelectricity because it allows us to strategically control where, when and how much the graphene is deformed by an applied electrical field with promising implications for engineering," said Ong.
While the results in creating piezoelectric graphene are encouraging, the researchers believe that their technique might further be used to engineer piezoelectricity in nanotubes and other nanomaterials with applications ranging from electronics, photonics, and energy harvesting to chemical sensing and high-frequency acoustics.
"We're already looking at new piezoelectric devices based on other 2D and low-dimensional materials, hoping they might open new and dramatic possibilities in nanotechnology," said Reed.
The Army High Performance Computing Research Center at Stanford University and the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory supported this research.
Listen to Reed and Ong talk about their work with ACS Nano: /www.stanford.edu/group/evanreed/media/ancac3-0212.mp3
Andrew Myers is the associate director of communications for the Stanford University School of Engineering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrew Myers
Associate Director of Communications
650.736.2245
Jamie Beckett
Director of Communications and Alumni Relations
650.736.2241
Copyright © Stanford School of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








