Home > Press > ORNL experiments prove nanoscale metallic conductivity in ferroelectrics
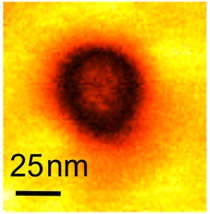 |
| ORNL researchers used piezoresponse force microscopy to demonstrate the first evidence of metallic conductivity in ferroelectric nanodomains. A representative nanodomain is shown in the PFM image above. |
Abstract:
The prospect of electronics at the nanoscale may be even more promising with the first observation of metallic conductance in ferroelectric nanodomains by researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
ORNL experiments prove nanoscale metallic conductivity in ferroelectrics
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on January 9th, 2012Ferroelectric materials, which switch their polarization with the application of an electric field, have long been used in devices such as ultrasound machines and sensors. Now, discoveries about ferroelectrics' electronic properties are opening up possibilities of applications in nanoscale electronics and information storage.
In a paper published in the American Chemical Society's Nano Letters, the ORNL-led team demonstrated metallic conductivity in a ferroelectric film that otherwise acts as an insulator. This phenomenon of an insulator-metal transition was predicted more than 40 years ago by theorists but has eluded experimental proof until now.
"This finding unambiguously identifies a new conduction channel that percolates through the insulating matrix of the ferroelectric, which opens potentially exciting possibilities to 'write' and 'erase' circuitry with nanoscale dimensions," said lead author Peter Maksymovych of ORNL's Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences.
From an applied perspective, the ability to use only an electric field as a knob that tunes both the magnitude of metallic conductivity in a ferroelectric and the type of charge carriers is particularly intriguing. Doing the latter in a semiconductor would require a change of the material composition.
"Not only can we turn on metallic conductivity, but if you keep changing the bias dials, you can control the behavior very precisely," Maksymovych said. "And the smaller the nanodomain, the better it conducts. All this occurs in the exact same position of the material, and we can go from an insulator to a better metal or a worse metal in a heartbeat or faster. This is potentially attractive for applications, and it also leads to interesting fundamental questions about the exact mechanism of metallic conductivity."
Although the researchers focused their study on a well-known ferroelectric film called lead-zirconate titanate, they expect their observations will hold true for a broader array of ferroelectric materials.
"We also anticipate that extending our studies onto multiferroics, mixed-phase and anti-ferroelectrics will reveal a whole family of previously unknown electronic properties, breaking new ground in fundamentals and applications alike," said co-author and ORNL senior scientist Sergei Kalinin.
The samples used in the study were provided by the University of California at Berkeley. Co-authors on the paper are ORNL's Arthur Baddorf, UC Berkeley's Ying-Hao Chu, Ramamoorthy Ramesh and Pu Yu, and National Academy of Science of Ukraine's Eugene Eliseev and Anna Morozovska. The full paper, "Tunable Metallic Conductance in Ferroelectric Nanodomains," is available at pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/nl203349b.
Part of this work was supported by the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences at ORNL. CNMS is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers supported by the DOE Office of Science, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge and Sandia and Los Alamos national laboratories. For more information about the DOE NSRCs, please visit science.energy.gov/bes/suf/user-facilities/nanoscale-science-research-centers/. Work at the University of California, Berkeley, was supported by DOE's Office of Science and the Semiconductor Research Corporation. ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy's Office of Science.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Morgan McCorkle
Communications and Media Relations
865.574.7308
Copyright © Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Insurance
![]() Multi-million pound project to use nanotechnology to improve safety September 4th, 2015
Multi-million pound project to use nanotechnology to improve safety September 4th, 2015
![]() Research seeks alternatives for reducing bacteria in fresh produce using nanoengineering April 29th, 2015
Research seeks alternatives for reducing bacteria in fresh produce using nanoengineering April 29th, 2015
![]() Liquipel Adds Guarantee to Watersafe Nano-Coating Products at CES: Announced at Booth 25936, South Hall; Billions in Hardware Damage to Be Saved January 8th, 2013
Liquipel Adds Guarantee to Watersafe Nano-Coating Products at CES: Announced at Booth 25936, South Hall; Billions in Hardware Damage to Be Saved January 8th, 2013
![]() Emerging Risks Report: Examining the case for Insurance in Engineered Nanomaterials December 29th, 2010
Emerging Risks Report: Examining the case for Insurance in Engineered Nanomaterials December 29th, 2010
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








