Home > Press > University of Twente provides alternative to optical semiconductor amplifiers: Potential optical amplification of more than one hundredfold
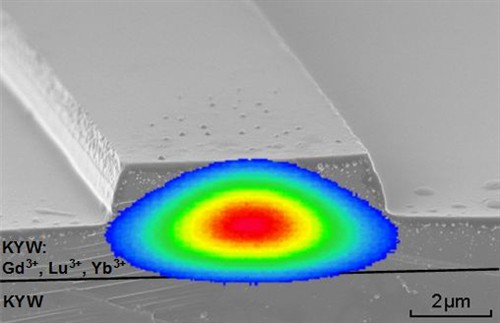 |
| Electron microscope image of a waveguide structure, superimposed with a measured intensity profile of the light trapped within it. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Twente's MESA+ research institute have developed a material capable of optical amplifications that are comparable to those achieved by the best, currently available semiconductor optical amplifiers. The researchers expect that this material will accelerate data communication and, ultimately, provide an alternative to short distance data communication (at the μm-cm scale). On 16 November, University of Twente researcher Dimitri Geskus will defend his PhD thesis based on this research, which he carried out at the Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science.
University of Twente provides alternative to optical semiconductor amplifiers: Potential optical amplification of more than one hundredfold
Enschede, The Netherlands | Posted on November 18th, 2011The increasingly exacting requirements being imposed on data communication are boosting demand for high-speed optical amplifiers. Current optical amplifiers suffer from the drawback that their speed is limited. Researchers at the university have now developed a material capable of optical amplifications which match those achieved using the best, currently available semiconductor optical amplifiers, but at potentially higher data communication rates. This material consists of thin crystalline layers whose optical properties were specially designed for the optical circuits found on chips. The researchers can fine-tune the properties of these thin crystalline layers by changing their composition. Using a clever trick, they were able to embed much higher concentrations of optically active Ytterbium ions (Ytterbium is a rare-earth element) in the crystal. In this way, they have boosted the optical amplification of currently available rare-earth-doped materials by more than one hundredfold. This will ultimately pave the way for faster and cheaper optical data communication.
PhD research
Dimitri Geskus carried out his PhD research at the MESA+ research institute's Integrated Optical Microsystems department. His work was supervised by Prof. Markus Pollnau. The research was partially funded by Prof. Pollnau's personal VICI grant from the Dutch Organization for Scientific Research (NWO).
Details of this work, drawn from Mr Geskus' dissertation, were recently published in the leading scientific journal Advanced Materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Science Information Officer
Joost Bruysters
(+31-(0)53-4892773/+31-(0)6 1048 8228)
Copyright © University of Twente
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








