Home > Press > Chemically assembled metamaterials could lead to superlenses and cloaking
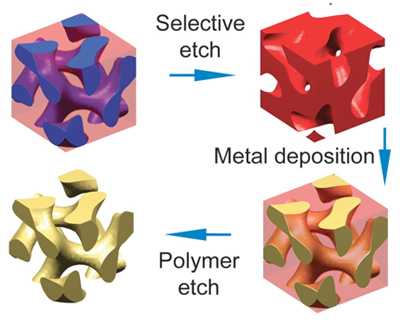 |
| Wiesner Lab Two polymer molecules linked together will self-assemble into a complex shape, in this case a convoluted "gyroid." One of the polymers is chemically removed, leaving a mold that can be filled with metal. Finally the other polymer is removed, leaving a metal gyroid with features measured in nanometers. |
Abstract:
Nanomanufacturing technology has enabled scientists to create metamaterials -- stuff that never existed in nature -- with unusual optical properties. They could lead to "superlenses" able to image proteins, viruses and DNA, and perhaps even make a "Star Trek" cloaking device.
Chemically assembled metamaterials could lead to superlenses and cloaking
Ithaca, NY | Posted on November 1st, 2011Other metamaterials offer unique magnetic properties that could have applications in microelectronics or data storage.
The limitation, so far, is that techniques like electron-beam lithography or atomic sputtering can only create these materials in thin layers. Now Cornell researchers propose an approach from chemistry to self-assemble metamaterials in three dimensions.
Uli Wiesner, the Spencer T. Olin Professor of Engineering, and colleagues present their idea in the online edition of the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Wiesner's research group offers a method they have pioneered in other fields, using block copolymers to self-assemble 3-D structures with nanoscale features.
A polymer is made up of molecules that chain together to form a solid or semisolid material. A block copolymer is made by joining two polymer molecules at the ends so that when each end chains up with others like itself, the two solids form an interconnected pattern of repeating geometric shapes -- planes, spheres, cylinders or a twisty network called a gyroid. Elements of the repeating pattern can be as small as a few nanometers across. Sometimes tri-polymers can be used to create even more complex shapes.
After the structure has formed, one of the two polymers can be dissolved away, leaving a 3-D mold that can be filled with a metal -- often gold or silver. Then the second polymer is burned away, leaving a porous metal structure.
In their paper the researchers propose to create metal gyroids that allow light to pass through, but are made up of nanoscale features that interact with light, just as the atoms in glass or plastic do. In this way, they say, it should be possible to design materials with a negative index of refraction, that is, materials that bend light in the opposite direction than in an ordinary transparent material.
Special lenses made of such a material could image objects smaller than the wavelength of visible light, including proteins, viruses and DNA. Some experimenters have made such superlenses, but so far none that work in the visible light range. Negative refraction materials might also be configured to bend light around an object -- at least a small one -- and make it invisible.
The Cornell researchers created computer simulations of several different metal gyroids that could be made by copolymer self-assembly, then calculated how light would behave when passing through these materials. They concluded that such materials could have a negative refractive index in the visible and near-infrared range. They noted that the amount of refraction could be controlled by adjusting the size of the repeating features of the metamaterial, which can be done by modifying the chemistry used in self-assembly.
They tried their calculations assuming the metal structures might be made of gold, silver or aluminum, and found that only silver produced satisfactory results.
Could these materials actually be made? According to graduate student Kahyun Hur, lead author on the paper, "We're working on it."
Hur's research is supported by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. Other aspects of the work have been funded by the National Science Foundation and the Computational Center for Nanotechnology Innovation at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Blaine Friedlander
(607) 254-8093
Bill Steele
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








