Home > Press > How Graphene’s Electrical Properties Can Be Tuned: Fortuitous discovery in UC Riverside physics lab made using stacked layers of “wonder material”
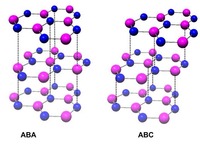 |
| In Bernal-stacked trilayer (ABA), the top (third) sheet is exactly on top of the lowest sheet. In rhombohedral-stacked (ABC) trilayer, the top sheet is shifted by the distance of an atom, so that the top (third) sheet and the lowest sheet form a Bernal stacking as well. Photo credit: Lau lab, UC Riverside. |
Abstract:
An accidental discovery in a physicist's laboratory at the University of California, Riverside provides a unique route for tuning the electrical properties of graphene, nature's thinnest elastic material. This route holds great promise for replacing silicon with graphene in the microchip industry.
How Graphene’s Electrical Properties Can Be Tuned: Fortuitous discovery in UC Riverside physics lab made using stacked layers of “wonder material”
Riverside, CA | Posted on September 26th, 2011The researchers found that stacking up three layers of graphene, like pancakes, significantly modifies the material's electrical properties. When they fabricated trilayer graphene in the lab and measured its conductance, they found, to their surprise, that depending on how the layers were stacked some of the trilayer graphene devices were conducting while others were insulating.
"What we stumbled upon is a simple and convenient ‘knob' for tuning graphene sheets' electrical properties," said Jeanie Lau, an associate professor of physics and astronomy, whose lab made the serendipitous finding.
Study results appeared online Sept. 25 in Nature Physics.
Graphene is a one-atom thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in hexagonal rings. Bearing excellent material properties, such as high current-carrying capacity and thermal conductivity, this "wonder material" is ideally suited for creating components for semiconductor circuits and computers.
Because of the planar and chicken wire-like structure of graphene, its sheets lend themselves well to stacking in what is called ‘Bernal stacking,' the stacking fashion of graphene sheets.
In a Bernal-stacked bilayer, one corner of the hexagons of the second sheet is located above the center of the hexagons of the bottom sheet. In Bernal-stacked trilayer (ABA), the top (third) sheet is exactly on top of the lowest sheet. In rhombohedral-stacked (ABC) trilayer, the top sheet is shifted by the distance of an atom, so that the top (third) sheet and the lowest sheet form a Bernal stacking as well.
"The most stable form of trilayer graphene is ABA, which behaves like a metal," Lau explained. "Amazingly, if we simply shift the entire topmost layer by the distance of a single atom, the trilayer - now with ABC or rhombohedral stacking - becomes insulating. Why this happens is not clear as yet. It could be induced by electronic interactions. We eagerly await an explanation from theorists!"
Her lab used Raman spectroscopy to examine the graphene devices' stacking orders. Next the lab plans to investigate the nature of the insulating state in ABC-stacked graphene. In this kind of stacked graphene, they also plan to study the band gap - a range in energy, critical for digital applications, in which no electrons can exist.
"The presence of the gap in ABC-stacked graphene that arises, we believe, from enhanced electronic interactions is interesting since it is not expected from theoretical calculations," Lau said. "Understanding this gap is particularly important for the major challenge of band gap engineering in graphene electronics."
Besides graphene, Lau studies nanowires and carbon nanotubes. Her research has helped physicists gain fundamental understanding of how atoms and electrons behave when they are ruled by quantum mechanics. Her lab studies novel electrical properties that arise from the quantum confinement of atoms and charges to nanoscale systems. Her research team has shown that graphene can act as an atomic-scale billiard table, with electric charges acting as billiard balls.
Her other research interests include superconductivity, thermal management and electronic transport in nanostructures, and engineering new classes of nanoscale devices.
An educational component of Lau's research effort is the active involvement of high school, undergraduate, and graduate students, especially minority and women, in her cutting-edge research, taking advantage of the ethnic diversity of UCR's student population and local communities. She is a founding faculty member of the UCR Undergraduate Research Journal. She also organized a "Women in Physics" lunch group that provides a friendly platform for female students, postdocs and faculty members to interact.
After receiving her bachelor's degree in physics from the University of Chicago in 1994, Lau proceeded to Harvard University from where she received her master's and doctoral degrees in physics in 1997 and 2001, respectively. She joined UCR in 2004, after an appointment as a research associate in the Hewlett-Packard Laboratory.
Lau's awards and honors include a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, 2009; a National Science Foundation CAREER Award, 2008; the Richter Fellowship for Undergraduate Research, 1992; a David W. Grainger Senior Scholarship, 1993; and a Robert T. Poe Faculty Development Grant from the Chinese-American Faculty Association of Southern California, 2007. She has published more than 60 research articles in peer-reviewed journals.
Lau, a member of UCR's Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering, was joined in the research by W. Bao (the first author of the research paper), L. Jing, J. Velasco Jr., Y. Lee, G. Liu, D. Tran and M. Bockrath at UCR; B. Stanley at Caltech; M. Aykol and S. B. Cronin at the University of Southern California; D. Smirnov at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Fla.; M. Koshino at Tohoku University, Japan; and E. McCann at Lancaster University, United Kingdom.
The research was funded by grants from the National Science Foundation, Office of Naval Research, and the Focus Center for Functional Engineered Nano Architectonics.
####
About University of California, Riverside
The University of California, Riverside (www.ucr.edu) is a doctoral research university, a living laboratory for groundbreaking exploration of issues critical to Inland Southern California, the state and communities around the world. Reflecting California's diverse culture, UCR's enrollment has exceeded 20,500 students. The campus will open a medical school in 2013 and has reached the heart of the Coachella Valley by way of the UCR Palm Desert Graduate Center. The campus has an annual statewide economic impact of more than $1 billion.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Iqbal Pittalwala
Tel: (951) 827-6050
Jeanie Lau
Copyright © University of California, Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Department of Physics and Astronomy:
Department of Physics and Astronomy:
![]() Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering:
Center for Nanoscale Science and Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








