Home > Press > UCSB Physicists Demonstrate the Quantum von Neumann Architecture, a Quantum Processor, and a Quantum Memory on a Chip
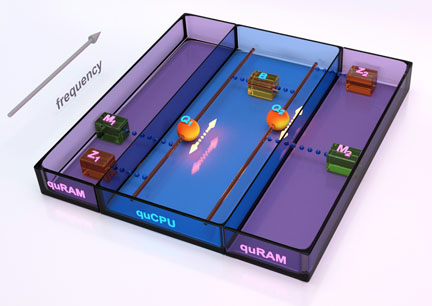 |
| The quantum von Neumann machine: Two qubits are coupled to a quantum bus, realizing a quCPU. Each qubit is accompanied by a quantum memory as well as a zeroing register. The quantum memories together with the zeroing register realize the quRAM. Credit: Peter Allen, UCSB |
Abstract:
A new paradigm in quantum information processing has been demonstrated by physicists at UC Santa Barbara. Their results are published in this week's issue of Science Express online.
UCSB Physicists Demonstrate the Quantum von Neumann Architecture, a Quantum Processor, and a Quantum Memory on a Chip
Santa Barbara, CA | Posted on September 1st, 2011UCSB physicists have demonstrated a quantum integrated circuit that implements the quantum von Neumann architecture. In this architecture, a long-lived quantum random access memory can be programmed using a quantum central processing unit, all constructed on a single chip, providing the key components for a quantum version of a classical computer.
The UCSB hardware is based on superconducting quantum circuits, and must be cooled to very low temperatures to display quantum behavior. The architecture represents a new paradigm in quantum information processing, and shows that quantum large-scale-integration is within reach.
The quantum integrated circuit includes two quantum bits (qubits), a quantum communication bus, two bits of quantum memory, and a resetting register comprising a simple quantum computer. "Computational steps take a few billionths of a second, comparable to a classical computer, but the great power is that a quantum computer can perform a large number of calculations simultaneously," said Matteo Mariantoni, postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Physics. "In our new UCSB architecture we have explored the possibility of writing quantum information to memory, while simultaneously performing other quantum calculations.
"On the quantum von Neumann architecture, we were able to run the quantum Fourier transform and a three-qubit Toffoli gate -- key quantum logic circuits for the further development of quantum computing," said Mariantoni.
The UCSB experiment was pursued primarily by Mariantoni, under the direction of Andrew N. Cleland and John M. Martinis, both professors of physics. Mariantoni was supported in this work by an Elings Prize Fellowship in Experimental Science from UCSB's California NanoSystems Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Gail Gallessich
(805)-893-7220
Matteo Mariantoni
(805) 893-5218
+39-338-7169569
skype name: matteo.mariantoni
Andrew Cleland
(805) 893-5401
John Martinis
(805) 893-3910
Copyright © UC Santa Barbara
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








