Home > Press > Nano bundles pack a powerful punch: Solid-state energy storage takes a leap forward at Rice University
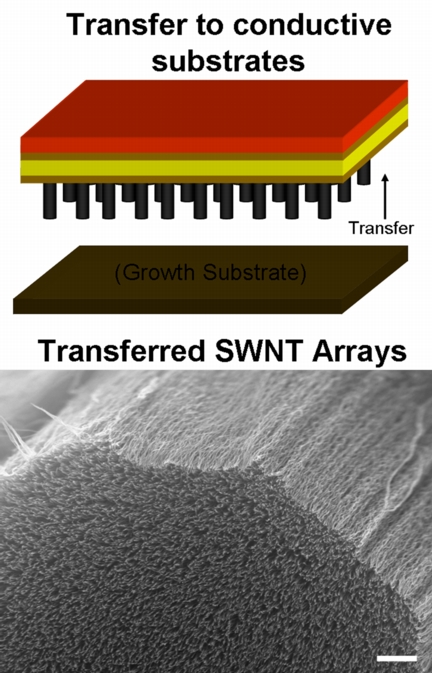 |
| A method developed at Rice University allows bundles of vertically aligned single-wall carbon nanotubes to be transferred intact to a conductive substrate. Metallic layers added via atomic layer deposition create a solid-state supercapacitor that can stand up in extreme environments. (Credit: Hauge Lab/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Rice University researchers have created a solid-state, nanotube-based supercapacitor that promises to combine the best qualities of high-energy batteries and fast-charging capacitors in a device suitable for extreme environments.
Nano bundles pack a powerful punch: Solid-state energy storage takes a leap forward at Rice University
Houston, TX | Posted on August 22nd, 2011A paper from the Rice lab of chemist Robert Hauge, to be published in the journal Carbon, reported the creation of robust, versatile energy storage that can be deeply integrated into the manufacture of devices. Potential uses span on-chip nanocircuitry to entire power plants.
Standard capacitors that regulate flow or supply quick bursts of power can be discharged and recharged hundreds of thousands of times. Electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), generally known as supercapacitors, are hybrids that hold hundreds of times more energy than a standard capacitor, like a battery, while retaining their fast charge/discharge capabilities.
But traditional EDLCs rely on liquid or gel-like electrolytes that can break down in very hot or cold conditions. In Rice's supercapacitor, a solid, nanoscale coat of oxide dielectric material replaces electrolytes entirely.
The researchers also took advantage of scale. The key to high capacitance is giving electrons more surface area to inhabit, and nothing on Earth has more potential for packing a lot of surface area into a small space than carbon nanotubes.
When grown, nanotubes self-assemble into dense, aligned structures that resemble microscopic shag carpets. Even after they're turned into self-contained supercapacitors, each bundle of nanotubes is 500 times longer than it is wide. A tiny chip may contain hundreds of thousands of bundles.
For the new device, the Rice team grew an array of 15-20 nanometer bundles of single-walled carbon nanotubes up to 50 microns long. Hauge, a distinguished faculty fellow in chemistry, led the effort with former Rice graduate students Cary Pint, first author of the paper and now a researcher at Intel, and Nolan Nicholas, now a researcher at Matric.
The array was then transferred to a copper electrode with thin layers of gold and titanium to aid adhesion and electrical stability. The nanotube bundles (the primary electrodes) were doped with sulfuric acid to enhance their conductive properties; then they were covered with thin coats of aluminum oxide (the dielectric layer) and aluminum-doped zinc oxide (the counterelectrode) through a process called atomic layer deposition (ALD). A top electrode of silver paint completed the circuit.
"Essentially, you get this metal/insulator/metal structure," said Pint. "No one's ever done this with such a high-aspect-ratio material and utilizing a process like ALD."
Hauge said the new supercapacitor is stable and scaleable. "All solid-state solutions to energy storage will be intimately integrated into many future devices, including flexible displays, bio-implants, many types of sensors and all electronic applications that benefit from fast charge and discharge rates," he said.
Pint said the supercapacitor holds a charge under high-frequency cycling and can be naturally integrated into materials. He envisioned an electric car body that is a battery, or a microrobot with an onboard, nontoxic power supply that can be injected for therapeutic purposes into a patient's bloodstream.
Pint said it would be ideal for use under the kind of extreme conditions experienced by desert-based solar cells or in satellites, where weight is also a critical factor. "The challenge for the future of energy systems is to integrate things more efficiently. This solid-state architecture is at the cutting edge," he said.
Co-authors of the paper include graduate student Zhengzong Sun; James Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and of computer science, and Howard Schmidt, adjunct assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, all of Rice; Sheng Xu, a former graduate student at Harvard; and Roy Gordon, the Thomas Dudley Cabot Professor of Chemistry at Harvard University, who developed ALD.
The research was supported by T.J. Wainerdi and Quantum Wired, in coordination with the Houston Area Research Council; the Office of Naval Research MURI program; the Wright Patterson Air Force Laboratory and the National Science Foundation.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 285-acre forested campus in Houston, Texas, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is known for its “unconventional wisdom." With 3,485 undergraduates and 2,275 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is less than 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 4 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to futureowls.rice.edu/images/futureowls/Rice_Brag_Sheet.pdf.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








