Home > Press > New nanostructured glass for imaging and recording
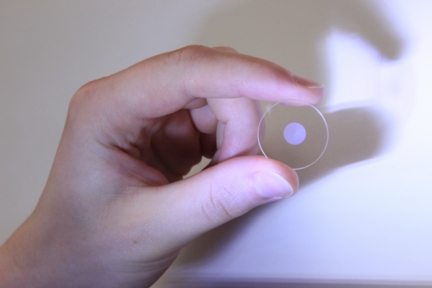 |
| New monolithic glass space-variant polarization converter |
Abstract:
University of Southampton researchers have developed new nano-structured glass optical elements, which have applications in optical manipulation and will significantly reduce the cost of medical imaging.
New nanostructured glass for imaging and recording
Southampton, UK | Posted on August 15th, 2011In a paper entitled Radially polarized optical vortex converter created by femtosecond laser nanostructuring of glass published in Applied Physics Letters, a team led by Professor Peter Kazansky at the University's Optoelectronics Research Centre, describe how they have used nano-structures to develop new monolithic glass space-variant polarization converters. These millimetre-sized devices generate ‘whirlpools' of light enabling: precise laser material processing, optical manipulation of atom-sized objects, ultra-high resolution imaging and potentially, table-top particle accelerators. They have since found that the technology can be developed further for optical recording.
According to the researchers, at sufficient intensities, ultra-short laser pulses can be used to imprint tiny dots (like 3D pixels) called voxels in glass. Their previous research showed that lasers with fixed polarization produce voxels consisting of a periodic arrangement of ultra-thin (tens of nanometers) planes. By passing polarized light through such a voxel imprinted in silica glass, the researchers observed that it travels differently depending on the polarization orientation of the light. This ‘form birefringence' phenomenon is the basis of their new polarization converter.
The advantage of this approach over existing methods for microscopy is that it is 20 times cheaper and it is compact.
"Before this we had to use a spatial light modulator based on liquid crystal which cost about £20,000," said Professor Peter Kazansky. "Instead we have just put a tiny device into the optical beam and we get the same result."
Since publication of the paper in May this year, the researchers have developed this technology further and adapted it for a five dimensional optical recording.
"We have improved the quality and fabrication time and we have developed this five dimensional memory which means that data can be stored on the glass and last forever," said Martynas Beresna, lead researcher for the project. "No one has ever done this before."
The researchers are working with the Lithuanian company Altechna to introduce this technology to the market.
####
About University of Southampton
The University of Southampton is a leading UK teaching and research institution with a global reputation for research and scholarship across a wide range of subjects in engineering, science, social sciences, health, arts and humanities.
With over 22,000 students, around 5000 staff, and an annual turnover well in excess of £400 million, the University of Southampton is one of the country's top institutions for engineering, computer science and medicine. It combines academic excellence with an innovative and entrepreneurial approach to research, supporting a culture that engages and challenges students and staff in their pursuit of learning.
The University is also home to a number of world-leading research centres, including the Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, the Optoelectronics Research Centre, the Centre for the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease, the Southampton Statistical Sciences Research Institute and is a partner of the National Oceanography Centre at the Southampton waterfront campus.
About The Optoelectronics Research Centre
The Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) is one of the world’s leading institutes for photonics research based at the University of Southampton. Over the last 40 years, the group has contributed significantly to the growth of the photonics industry.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Helene Murphy
Media Relations Consultant to the University of Southampton
+44(0)20 8531 8000
+44(0)7944 847570
Martynas Beresna
Optoelectronics Research Centre
University of Southampton
Tel: 44 07930863262
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








