Home > Press > Insect Virus Holds the Key to Safer Stem Cell Therapy: IBN's New Genetic Engineering Technique Aims to Benefit Cancer Patients
 |
Abstract:
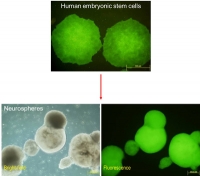
The future of regenerative medicine lies in harnessing the potential of the human body to renew and repair itself. Now, scientists at the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN), the world's first bioengineering and nanotechnology research institute, have developed a new genetic engineering technique that promises safer stem cell therapy for cancer patients. Using an insect virus, the team of researchers successfully inserted a therapeutic gene into a safe site in the DNA of human embryonic stem cells without compromising the functionality of the engineered cells.
Insect Virus Holds the Key to Safer Stem Cell Therapy: IBN's New Genetic Engineering Technique Aims to Benefit Cancer Patients
Singapore | Posted on July 28th, 2011Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells have the unique ability to transform themselves into any cell type, making them attractive candidates for cell-based therapies in regenerative medicine. Many medical applications require the integration of therapeutic genes into these stem cells before they are transplanted into the patient. However, current genetic engineering techniques lack accuracy and are not effective enough in ensuring that the therapeutic genes would function properly after they are integrated into chromosomes of the stem cells.
The most commonly used method of introducing transgenes into hESCs is random integration. This is a technique that could result in unwanted mutations, and possibly even tumor formation of the transplanted cells. It would also be difficult to predict whether the randomly inserted transgene would be able to function properly, as certain DNA sequences may trigger a malfunction or completely 'shut down' the gene. Therefore, there is a compelling need to develop a new technique that provides better control over the precise location of gene integration without affecting the genomic stability.
Previous studies have identified the adeno-associated virus integration site 1 locus (AAVS1) as a ‘safe harbor' for the addition of a new gene into the human genome as there is no known adverse effect on the cell resulting from gene disruption at this site, and the inserted gene has been shown to retain its competence across diverse cell types. Two known methods of delivering genes directly into AAVS1 utilize the AAV2 technology and the zinc-finger nuclease technology. The former has a very low targeting efficiency rate of 4%, indicating a very high risk of random gene insertion. Despite the improved targeting efficiency of the latter (33-61%), it could be toxic to cells and not ideal for use in vivo.
According to IBN Group Leader, Dr Shu Wang, "Having observed the technical complications that plague cell-based therapy, we decided to find a way to enhance the safety and unearth the true potential of this form of therapy for disease treatment. Our lab has been developing stem cell-based vehicles for cancer therapy over the last few years, and we needed a safe method to introduce tumor-killing therapeutic genes into stem cells."
IBN's technique has been shown to achieve up to 100% targeting accuracy, and the IBN researchers are the first to demonstrate homology recombination at the AAVS1 site in hES cells, and to combine the use of baculoviral vectors with the Cre/loxP recombinase system to target and splice specific DNA sequences in these cells.
"As baculoviruses are insect viruses that are known not to insert themselves into human genomes randomly, our method is also much safer than using AAV2 and zinc-finger nuclease, as it causes little or no toxicity to the hES cells," added Dr Wang. "We hope that someday, cells derived from those iPS cells that are genetically modified with our method could be used clinically for cancer therapy."
Published recently in Nucleic Acids Research, IBN's novel genetic engineering technique has great potential to advance the field of stem cell research, benefiting both basic science researchers and clinician scientists. The method developed by the IBN researchers allows repeated insertion of genes at the AAVS1 site, presenting the opportunity to introduce a variety of therapeutic genes safely into the genome of hESCs and iPS cells for various medical applications. The modified hESCs can also be used as a starting material for generating transgenic hESCs for research, significantly reducing the amount of time spent on screening modified hESC clones.
"Using a new and better technology to treat chronic and degenerative diseases is the driving force behind our gene delivery research at IBN. Stem cell based therapy is one of our key research thrusts and we hope to unravel its potential to transform medical treatments with our innovative genetic modification approach," added Professor Jackie. Y. Ying, IBN Executive Director.
Reference: C. J. A. Ramachandra, M. Shahbazi, T. W. X. Kwang, Y. Choudhury, X. Y. Bak, J. Yang and S. Wang, "Efficient Recombinase-Mediated Cassette Exchange at the AAVS1 Locus in Human Embryonic Stem Cells Using Baculoviral Vectors, " Nucleic Acids Research, (2011) DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr409.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nidyah Sani
Tel: 65 6824 7005
Copyright © The Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








