Home > Press > Good Eggs: Nanomagnets are Food for Thought on Computer Memories
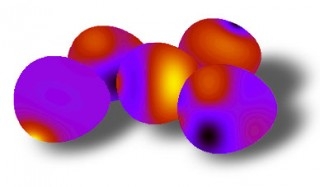 |
| Collage of NIST "nano-eggs" — simulated magnetic patterns in NIST’s egg-shaped nanoscale magnets. |
Abstract:
Magnetics researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) colored lots of eggs recently. Bunnies and children might find the eggs a bit small—in fact, too small to see without a microscope. But these "eggcentric" nanomagnets have another practical use, suggesting strategies for making future low-power computer memories.
Good Eggs: Nanomagnets are Food for Thought on Computer Memories
Boulder, CO | Posted on April 28th, 2011For a study described in a new paper,* NIST researchers used electron-beam lithography to make thousands of nickel-iron magnets, each about 200 nanometers (billionths of a meter) in diameter. Each magnet is ordinarily shaped like an ellipse, a slightly flattened circle. Researchers also made some magnets in three different egglike shapes with an increasingly pointy end. It's all part of NIST research on nanoscale magnetic materials, devices and measurement methods to support development of future magnetic data storage systems.
It turns out that even small distortions in magnet shape can lead to significant changes in magnetic properties. Researchers discovered this by probing the magnets with a laser and analyzing what happens to the "spins" of the electrons, a quantum property that's responsible for magnetic orientation. Changes in the spin orientation can propagate through the magnet like waves at different frequencies. The more egg-like the magnet, the more complex the wave patterns and their related frequencies. (Something similar happens when you toss a pebble in an asymmetrically shaped pond.) The shifts are most pronounced at the ends of the magnets.
To confirm localized magnetic effects and "color" the eggs, scientists made simulations of various magnets using NIST's object-oriented micromagnetic framework (OOMMF).** (See graphic.) Lighter colors indicate stronger frequency signals.
The egg effects explain erratic behavior observed in large arrays of nanomagnets, which may be imperfectly shaped by the lithography process. Such distortions can affect switching in magnetic devices. The egg study results may be useful in developing random-access memories (RAM) based on interactions between electron spins and magnetized surfaces. Spin-RAM is one approach to making future memories that could provide high-speed access to data while reducing processor power needs by storing data permanently in ever-smaller devices. Shaping magnets like eggs breaks up a symmetric frequency pattern found in ellipse structures and thus offers an opportunity to customize and control the switching process.
"For example, intentional patterning of egg-like distortions into spinRAM memory elements may facilitate more reliable switching," says NIST physicist Tom Silva, an author of the new paper.
"Also, this study has provided the Easter Bunny with an entirely new market for product development."
---------------------------------
* H.T. Nembach, J.M. Shaw, T.J. Silva, W.L. Johnson, S.A. Kim, R.D. McMichael and P. Kabos. Effects of shape distortions and imperfections on mode frequencies and collective linewidths in nanomagnets. Physical Review B 83, 094427, March 28, 2011.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Ost
(303) 497-4880
Copyright © NIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() ** See http://math.nist.gov/oommf/
** See http://math.nist.gov/oommf/
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








