Home > Press > Engineers grow nanolasers on silicon, pave way for on-chip photonics
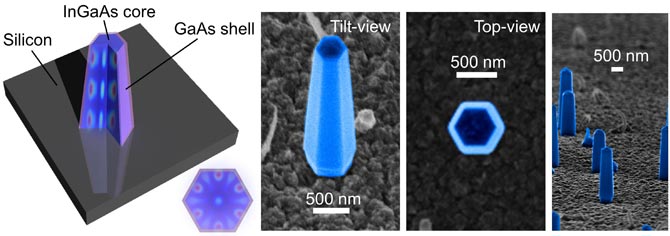 |
| Shown is a schematic (left) and various scanning electron microscope images of nanolasers grown directly on a silicon surface. The achievement could lead to a new class of optoelectronic chips. (Courtesy Connie Chang-Hasnain Group) |
Abstract:
Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have found a way to grow nanolasers directly onto a silicon surface, an achievement that could lead to a new class of faster, more efficient microprocessors, as well as to powerful biochemical sensors that use optoelectronic chips.
They describe their work in a paper to be published Feb. 6 in an advanced online issue of the journal Nature Photonics.
By Sarah Yang
Engineers grow nanolasers on silicon, pave way for on-chip photonics
Berkeley, CA | Posted on February 6th, 2011"Our results impact a broad spectrum of scientific fields, including materials science, transistor technology, laser science, optoelectronics and optical physics," said the study's principal investigator, Connie Chang-Hasnain, UC Berkeley professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences.
The increasing performance demands of electronics have sent researchers in search of better ways to harness the inherent ability of light particles to carry far more data than electrical signals can. Optical interconnects are seen as a solution to overcoming the communications bottleneck within and between computer chips.
Because silicon, the material that forms the foundation of modern electronics, is extremely deficient at generating light, engineers have turned to another class of materials known as III-V (pronounced "three-five") semiconductors to create light-based components such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and lasers.
But the researchers pointed out that marrying III-V with silicon to create a single optoelectronic chip has been problematic. For one, the atomic structures of the two materials are mismatched.
"Growing III-V semiconductor films on silicon is like forcing two incongruent puzzle pieces together," said study lead author Roger Chen, a UC Berkeley graduate student in electrical engineering and computer sciences. "It can be done, but the material gets damaged in the process."
Moreover, the manufacturing industry is set up for the production of silicon-based materials, so for practical reasons, the goal has been to integrate the fabrication of III-V devices into the existing infrastructure, the researchers said.
"Today's massive silicon electronics infrastructure is extremely difficult to change for both economic and technological reasons, so compatibility with silicon fabrication is critical," said Chang-Hasnain. "One problem is that growth of III-V semiconductors has traditionally involved high temperatures - 700 degrees Celsius or more - that would destroy the electronics. Meanwhile, other integration approaches have not been scalable."
The UC Berkeley researchers overcame this limitation by finding a way to grow nanopillars made of indium gallium arsenide, a III-V material, onto a silicon surface at the relatively cool temperature of 400 degrees Celsius.
"Working at nanoscale levels has enabled us to grow high quality III-V materials at low temperatures such that silicon electronics can retain their functionality," said Chen.
The researchers used metal-organic chemical vapor deposition to grow the nanopillars on the silicon. "This technique is potentially mass manufacturable, since such a system is already used commercially to make thin film solar cells and light emitting diodes," said Chang-Hasnain.
Once the nanopillar was made, the researchers showed that it could generate near infrared laser light - a wavelength of about 950 nanometers - at room temperature. The hexagonal geometry dictated by the crystal structure of the nanopillars creates a new, efficient, light-trapping optical cavity. Light circulates up and down the structure in a helical fashion and amplifies via this optical feedback mechanism.
The unique approach of growing nanolasers directly onto silicon could lead to highly efficient silicon photonics, the researchers said. They noted that the miniscule dimensions of the nanopillars - smaller than one wavelength on each side, in some cases - make it possible to pack them into small spaces with the added benefit of consuming very little energy
"Ultimately, this technique may provide a powerful and new avenue for engineering on-chip nanophotonic devices such as lasers, photodetectors, modulators and solar cells," said Chen.
"This is the first bottom-up integration of III-V nanolasers onto silicon chips using a growth process compatible with the CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) technology now used to make integrated circuits," said Chang-Hasnain. "This research has the potential to catalyze an optoelectronics revolution in computing, communications, displays and optical signal processing. In the future, we expect to improve the characteristics of these lasers and ultimately control them electronically for a powerful marriage between photonic and electronic devices."
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and a Department of Defense National Security Science and Engineering Faculty Fellowship helped support this research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Connie Chang-Hasnain
(650) 799-7355
Roger Chen
(508) 561-8213
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








