Home > Press > Touchscreens Made of Carbon
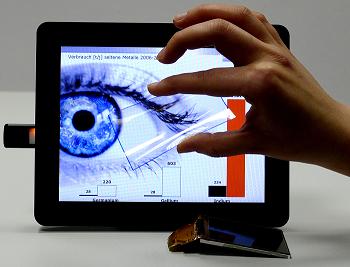 |
| Touchscreen that contain carbon nanotubes can be made of low-priced renewable materials |
Abstract:
Touchscreens are in - although the technology still has its price. The little screens contain rare and expensive elements. This is the reason why researchers at Fraunhofer are coming up with an alternative display made of low-priced renewable raw materials available all over the world. The researchers are presenting touchscreens that contain carbon nanotubes at the nano tech 2011 fair in Tokyo (Hall 5, Stand E-18-11) from February 16-18.
Touchscreens Made of Carbon
Munich, Germany | Posted on January 28th, 2011Just touching it slightly with the tips of your fingers is enough. You can effortlessly write, navigate, open menu windows or rotate images on touchscreens. Within fractions of a second your touch is translated into control commands that a computer understands. At first glance, this technology borders on the miraculous, but in real life this mystery just is a wafer-thin electrode under the glass surface of the display made of indium-tin-oxide, ITO. This material is nothing short of ideal for use in touchscreens because it is excellent at conducting slight currents and lets the colors of the display pass through unhindered. But, there is a little problem: there are very few deposits of indium anywhere in the world. In the long term, the manufacturers of electronic gadgets are afraid that they will be dependent upon the prices set by suppliers. This is the reason why indium is one of what people call "strategic metals."
Therefore, private industry is very interested in alternatives to ITO that are similarly efficient. The researchers at Fraunhofer have succeeded at coming up with a new material for electrodes that is on the same level as ITO and on top of it is much cheaper. Its main components are carbon nanotubes and low-cost polymers. This new electrode foil is composed of two layers. One is the carrier, a thin foil made of inexpensive polyethylenterephthalate PET used for making plastic bottles. Then a mixture of carbon-nanotubes and electrically conducting polymers is added that is applied to the PET as a solution and forms a thin film when it dries.
In comparison to ITO, these combinations of plastics have not been particularly durable because humidity, pressure or UV light put a strain on the polymers. The layers became brittle and broke down. Only carbon nanotubes have made them stable. The carbon nanotubes harden on the PET to create a network where the electrically conducting polymers can be firmly anchored. That means that this layer is durable in the long run. Ivica Kolaric, project manager from Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA, concedes that "the electrical resistance of our layer is somewhat greater than that of the ITO, but it's easily enough for an application in electrical systems." Its merits are unbeatable: carbon is not only low-cost and available all over the world. It is also a renewable resource that you can get from organic matter such as wood. Kolaric and his colleagues will be presenting their carbon touchdisplay at the 2011 nano tech fair. Since 2003 Fraunhofer researchers show their developments at the annual trade show.
There are a whole series of implementations for the new technology. This foil is flexible and can be used in a variety of ways. Kolaric sums up by saying "we could even make photovoltaic foils out of it to line corrugated roofs or other uneven structures." The researcher has already set up pilot production where the foil can be enhanced for a wide range of applications.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Franz Miller
Head of Press and Public Relations
Headquarters of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
Hansastraße 27c
80686 Munich, Germany
franz.miller(at)zv.fraunhofer.de
Phone +49 89 1205-1300
Fax +49 89 1205-7515
Copyright © Fraunhofer Institute
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








