Home > Press > Vibrating nanorods measure thin films for microcircuits
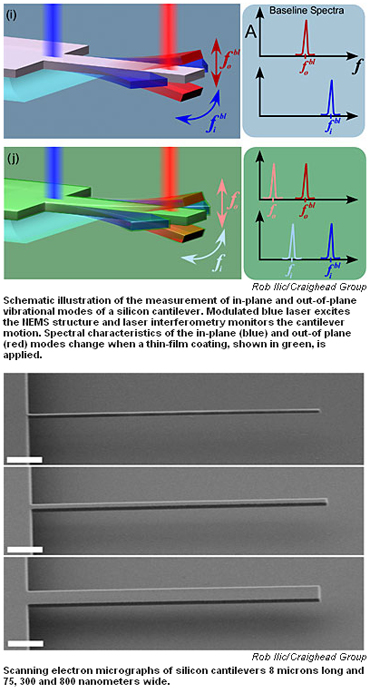 |
Abstract:
A key step in many nanofabrication processes is to create thin films, sometimes only one molecule thick, by a method known as atomic layer deposition. Researchers at Cornell and Tel Aviv University have developed a new tool for nanofabricators to test the physical properties of such films.
By Bill Steele
Vibrating nanorods measure thin films for microcircuits
Ithaca, NY | Posted on December 11th, 2010Ultrathin films are increasingly important in constructing microcircuits. Their physical characteristics often determine their electronic behavior as well as their resistance to wear.
The researchers have shown that tiny resonant cantilevers -- silicon rods anchored at one end, like a tiny diving board -- can determine the density of a film and its Young's modulus, a measure of resistance to bending. The method offers several advantages over other methods of measuring these characteristics of thin films, the researchers said, and can be used by any researchers with access to nanofabrication capabilities comparable to those at the Cornell Nanoscale Facility.
The work was reported in the Aug. 15 issue of the Journal of Applied Physics by Cornell research associate Rob Ilic, Slava Krylov, senior lecturer at Tel Aviv University and former visiting professor at Cornell, and Harold Craighead, the C.W. Lake Jr. Professor of Engineering at Cornell.
Cornell researchers have previously used tiny vibrating cantilevers just a few nanometers (billionths of a meter) thick to detect the mass of objects as small as a virus. Just as a thick guitar string vibrates at a lower note than a thinner one, adding mass to a vibrating rod changes its frequency of vibration. Coating the rod with a thin film adds detectable mass, and from the mass and thickness of the film, density can be determined.
The film also changes the cantilever's resistance to bending. To separate out this characteristic, the researchers compared in-plane (side to side) and out-of-plane (up and down) vibrations. The resistance to bending in different directions is noticeably different when the vibrating rod is wide and thin. When the cross-section of the rod is square, there is no difference between up and down and side-to-side movement.
To test their idea, the researchers fabricated a variety of cantilevers six to 10 microns (millionths of a meter) long, 45 nanometers thick and with widths varying from 45 nanometers to 1 micron. In various experiments, they applied films of aluminum, aluminum nitride and hafnium from 21.2 to 21.5 nanometers thick to the surface of the cantilevers.
A laser beam focused on the base of a cantilever supplies energy to set it vibrating, and another laser aimed at the end measures the vibration. Like a tuning fork, each rod has a resonant frequency at which it vibrates, and that depends on the dimensions and physical characteristics of the device. Comparing the resonant frequency and some of its harmonics before and after a film was applied enabled the researchers to calculate the density and Young's modulus of the film.
Over many experiments, the calculations agreed well with theoretical predictions and characteristics of films measured by other methods. Some aspects of the method of fabricating the nanocantilevers could affect the results, the researchers found, but they said accuracy could be improved.
The work was supported by the Defense Advanced Projects Research Administration, the National Science Foundation and the state of New York.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact:
Joe Schwartz
(607) 254-6235
Cornell Chronicle:
Bill Steele
(607) 255-7164
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








