Home > Press > Triple-mode transistors show potential
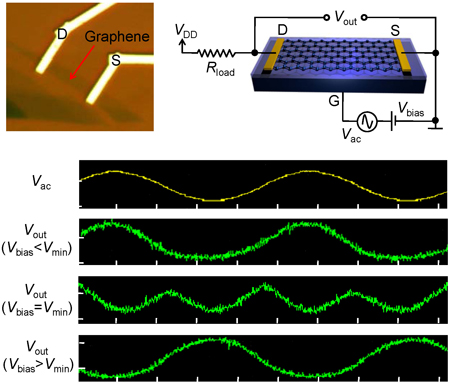 |
| Top left: A graphene transistor with source and drain electrodes; top right, a schematic for the triple-mode single-transistor graphene amplifier; and bottom, a graph showing the three distinct modes of operation. (Images: Mohanram Lab/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Rice researchers introduce graphene-based amplifiers
Triple-mode transistors show potential
Houston, TX | Posted on October 13th, 2010Rice University research that capitalizes on the wide-ranging capabilities of graphene could lead to circuit applications that are far more compact and versatile than what is now feasible with silicon-based technologies.
Triple-mode, single-transistor amplifiers based on graphene -- the one-atom-thick form of carbon that recently won its discoverers a Nobel Prize -- could become key components in future electronic circuits. The discovery by Rice researchers was reported this week in the online journal ACS Nano.
Graphene is very strong, nearly transparent and conducts electricity very well. But another key property is ambipolarity, graphene's ability to switch between using positive and negative carriers on the fly depending on the input signal. Traditional silicon transistors usually use one or the other type of carrier, which is determined during fabrication.
A three-terminal single-transistor amplifier made of graphene can be changed during operation to any of three modes at any time using carriers that are positive, negative or both, providing opportunities that are not possible with traditional single-transistor architectures, said Kartik Mohanram, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Rice. He collaborated on the research with Alexander Balandin, a professor of electrical engineering at the University of California, Riverside, and their students Xuebei Yang (at Rice) and Guanxiong Liu (at Riverside).
Mohanram likened the new transistor's abilities to that of a water tap. "Turn it on and the water flows," he said. "Turn it off and the water stops. That's what a traditional transistor does. It's a unipolar device -- it only opens and closes in one direction."
"But if you close a tap too much, it opens again and water flows. That's what ambipolarity is -- current can flow when you open the transistor in either direction about a point of minimum conduction."
That alone means a graphene transistor can be "n-type" (negative) or "p-type" (positive), depending on whether the carrier originates from the source or drain terminals (which are effectively interchangeable). A third function appears when the input from each carrier is equal: The transistor becomes a frequency multiplier. By combining the three modes, the Rice-Riverside team demonstrated such common signaling schemes as phase and frequency shift keying for wireless and audio applications.
"Our work, and that of others, that focuses on the applications of ambipolarity complements efforts to make a better transistor with graphene," Mohanram said. "It promises more functionality." The research demonstrated that a single graphene transistor could potentially replace many in a typical integrated circuit, he said. Graphene's superior material properties and relative compatibility with silicon-based manufacturing should allow for integration of such circuits in the future, he added.
Technological roadblocks need to be overcome, Mohanram said. Such fabrication steps as dielectric deposition and making contacts "wind up disturbing the lattice, scratching it and introducing defects. That immediately degrades its performance (limiting signal gain), so we have to exercise a lot of care in fabrication.
"But the technology will mature, since so many research groups are working hard to address these challenges," he said.
The National Science Foundation and the DARPA-Semiconductor Research Corporation's Focus Center Research Program supported the work.
Read the abstract at pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nn1021583.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








